Evolving impact of long-term survival results on metastatic melanoma treatment
- PMID: 33037115
- PMCID: PMC7549477
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000948
Evolving impact of long-term survival results on metastatic melanoma treatment
Abstract
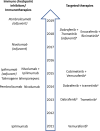
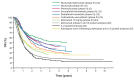
Melanoma treatment has been revolutionized over the past decade. Long-term results with immuno-oncology (I-O) agents and targeted therapies are providing evidence of durable survival for a substantial number of patients. These results have prompted consideration of how best to define long-term benefit and cure. Now more than ever, oncologists should be aware of the long-term outcomes demonstrated with these newer agents and their relevance to treatment decision-making. As the first tumor type for which I-O agents were approved, melanoma has served as a model for other diseases. Accordingly, discussions regarding the value and impact of long-term survival data in patients with melanoma may be relevant in the future to other tumor types. Current findings indicate that, depending on the treatment, over 50% of patients with melanoma may gain durable survival benefit. The best survival outcomes are generally observed in patients with favorable prognostic factors, particularly normal baseline lactate dehydrogenase and/or a low volume of disease. Survival curves from melanoma clinical studies show a plateau at 3 to 4 years, suggesting that patients who are alive at the 3-year landmark (especially in cases in which treatment had been stopped) will likely experience prolonged cancer remission. Quality-of-life and mixture-cure modeling data, as well as metrics such as treatment-free survival, are helping to define the value of this long-term survival. In this review, we describe the current treatment landscape for melanoma and discuss the long-term survival data with immunotherapies and targeted therapies, discussing how to best evaluate the value of long-term survival. We propose that some patients might be considered functionally cured if they have responded to treatment and remained treatment-free for at least 2 years without disease progression. Finally, we consider that, while there have been major advances in the treatment of melanoma in the past decade, there remains a need to improve outcomes for the patients with melanoma who do not experience durable survival.
Keywords: CTLA-4 antigen; immunomodulation; immunotherapy; programmed cell death 1 receptor; review.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: OM: Consulting or advisory role: Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, and Roche. Travel, accommodations, and expenses: Bristol Myers Squibb and Merck Sharp & Dohme. Expert testimony: Bristol Myers Squibb. Research funding: Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and NeraCare GmbH. MBA: Advisory board: Arrowhead, Bristol Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Fathom, Leads, Merck, Novartis, PACT, Pfizer, Pneuma, Pyxis Oncology, and Werewolf. Consultant: Array, Aveo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cota, Eisai, Galactone (personal fees), Genentech/Roche, ImmunoCore, Iovance, Merck, Newlink, Novartis, Pfizer, and Surface. Research support to institution: Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, and Pfizer. Clinical trial involvement: Aveo (Tivo 3), Bristol Myers Squibb (CM-214, CM-004, CM-067, CM-204, CM-218, CM-238, CM-905, X4P-X4 RCCA, X4-RCCB), Genentech/Roche (ImMotion 150, ImMotion 151), Merck (KN- 426, KN-427, KN-029, KN-564), and Pfizer (029 Trial, Javelin 101). Speaker’s bureau: None. Stock options: Pyxis Oncology and Werewolf. HBK: Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb. Stock and other ownership interests: Bristol Myers Squibb. RD: Consulting or advisory role: Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and Takeda. Honoraria: Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and Takeda. Research funding: Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, and Roche. PAA: Consulting or advisory role: 4SC, Alkermes, Amgen, Array BioPharma, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genmab, Idera, Immunocore, Incyte, Italfarmaco, MedImmune, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Nektar, NewLink Genetics, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Roche/Genentech, Sandoz, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, Syndax, and Ultimovacs. Travel, accommodations, and expenses: Merck Sharp & Dohme. Stock and other ownership interests: PrimeVax. Research funding: Array BioPharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Roche/Genentech.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
