Integrative genomic analysis reveals mechanisms of immune evasion in P. falciparum malaria
- PMID: 33037226
- PMCID: PMC7547729
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18915-6
Integrative genomic analysis reveals mechanisms of immune evasion in P. falciparum malaria
Abstract
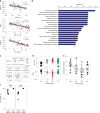
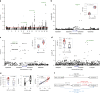
The mechanisms behind the ability of Plasmodium falciparum to evade host immune system are poorly understood and are a major roadblock in achieving malaria elimination. Here, we use integrative genomic profiling and a longitudinal pediatric cohort in Burkina Faso to demonstrate the role of post-transcriptional regulation in host immune response in malaria. We report a strong signature of miRNA expression differentiation associated with P. falciparum infection (127 out of 320 miRNAs, B-H FDR 5%) and parasitemia (72 miRNAs, B-H FDR 5%). Integrative miRNA-mRNA analysis implicates several infection-responsive miRNAs (e.g., miR-16-5p, miR-15a-5p and miR-181c-5p) promoting lymphocyte cell death. miRNA cis-eQTL analysis using whole-genome sequencing data identified 1,376 genetic variants associated with the expression of 34 miRNAs (B-H FDR 5%). We report a protective effect of rs114136945 minor allele on parasitemia mediated through miR-598-3p expression. These results highlight the impact of post-transcriptional regulation, immune cell death processes and host genetic regulatory control in malaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2018. 210 (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

