Potential roles of medicinal plants for the treatment of viral diseases focusing on COVID-19: A review
- PMID: 33037698
- PMCID: PMC7675695
- DOI: 10.1002/ptr.6893
Potential roles of medicinal plants for the treatment of viral diseases focusing on COVID-19: A review
Abstract
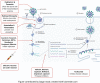
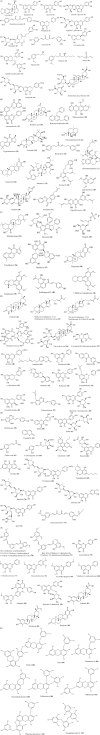
The whole world is entangled by the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), people are dying in thousands each day, and without an actual medication, it seems not possible for the bringing this global health crisis to a stop. Natural products have been in constant use since ancient times and are proven by time to be effective. Crude extract or pure compounds isolated from medicinal plants and/or herbs such as Artemisia annua, Agastache rugosa, Astragalus membranaceus, Cassia alata, Ecklonia cava, Gymnema sylvestre, Glycyrrhizae uralensis, Houttuynia cordata, Lindera aggregata, Lycoris radiata, Mollugo cerviana, Polygonum multiflorum, Pyrrosia lingua, Saposhnikoviae divaricate, Tinospora cordifolia etc. have shown promising inhibitory effect against coronavirus. Several molecules, including acacetin, amentoflavone, allicin, blancoxanthone, curcumin, daidzein, diosmin, epigallocatechin-gallate, emodin, hesperidin, herbacetin, hirsutenone, iguesterin, jubanine G, kaempferol, lycorine, pectolinarin, phloroeckol, silvestrol, tanshinone I, taxifolin, rhoifolin, xanthoangelol E, zingerol etc. isolated from plants could also be potential drug candidates against COVID-19. Moreover, these could also show promising inhibitory effects against influenza-parainfluenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Here, we have reported 93 antiviral drug candidates which could be a potential area of research in drug discovery.
Keywords: anti-antiviral activity and COVID-19; drug candidates; natural products.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Alagu Lakshmi, S. , Shafreen, R. M. B. , Priya, A. , & Shunmugiah, K. P. (2020). Ethnomedicines of Indian origin for combating COVID‐19 infection by hampering the viral replication: Using structure‐based drug discovery approach. Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics, 1–16. 10.1080/07391102.2020.1778537 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balzarini, J. , Keyaerts, E. , Vijgen, L. , Vandermeer, F. , Stevens, M. , De Clercq, E. , … Van Ranst, M. (2006). Pyridine N‐oxide derivatives are inhibitory to the human SARS and feline infectious peritonitis coronavirus in cell culture. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 57(3), 472–481. 10.1093/jac/dki481 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

