Targeting DNA Damage Response and Replication Stress in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 33039466
- PMCID: PMC8167930
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.043
Targeting DNA Damage Response and Replication Stress in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
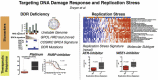
Background & aims: Continuing recalcitrance to therapy cements pancreatic cancer (PC) as the most lethal malignancy, which is set to become the second leading cause of cancer death in our society. The study aim was to investigate the association between DNA damage response (DDR), replication stress, and novel therapeutic response in PC to develop a biomarker-driven therapeutic strategy targeting DDR and replication stress in PC.
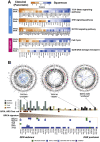
Methods: We interrogated the transcriptome, genome, proteome, and functional characteristics of 61 novel PC patient-derived cell lines to define novel therapeutic strategies targeting DDR and replication stress. Validation was done in patient-derived xenografts and human PC organoids.
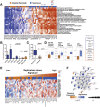
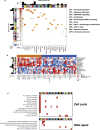
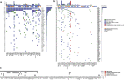
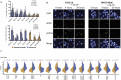
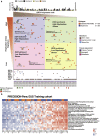
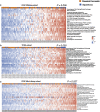
Results: Patient-derived cell lines faithfully recapitulate the epithelial component of pancreatic tumors, including previously described molecular subtypes. Biomarkers of DDR deficiency, including a novel signature of homologous recombination deficiency, cosegregates with response to platinum (P < .001) and PARP inhibitor therapy (P < .001) in vitro and in vivo. We generated a novel signature of replication stress that predicts response to ATR (P < .018) and WEE1 inhibitor (P < .029) treatment in both cell lines and human PC organoids. Replication stress was enriched in the squamous subtype of PC (P < .001) but was not associated with DDR deficiency.
Conclusions: Replication stress and DDR deficiency are independent of each other, creating opportunities for therapy in DDR-proficient PC and after platinum therapy.
Keywords: DNA Damage Response; Pancreatic Cancer; Personalized Medicine; Replication Stress.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L., Smith B.D., Aizenberg R. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- Bailey P., Chang D.K., Nones K. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2016;531(7592):47–52. - PubMed
Supplementary References
-
- Zhang J.H., Chung T.D., Oldenburg K.R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J Biomol Screen. 1999;4:67–73. - PubMed
-
- Parrish R.S., Spencer H.J., 3rd Effect of normalization on significance testing for oligonucleotide microarrays. J Biopharm Stat. 2004;14:575–589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 25813/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 30322/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- A23526/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C29717/A18484/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C596/A20921/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P50 CA102701/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C596/A18076/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 25714/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 27820/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P50 CA062924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 103721/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 CA150190/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16354/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 21139/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 29996/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C29717/A17263/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

