Cytokines and transcription factors in the differentiation of CD4+ T helper cell subsets and induction of tissue inflammation and autoimmunity
- PMID: 33039897
- PMCID: PMC7747296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2020.09.001
Cytokines and transcription factors in the differentiation of CD4+ T helper cell subsets and induction of tissue inflammation and autoimmunity
Abstract
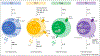
CD4+T helper (Th) cells are critical in homeostasis and host defense but are also central to the development of various autoimmune diseases if they become dysregulated. Specifically, pathogenic Th1 and Th17 cells contribute to autoimmune inflammation whereas Treg and Tr1 cells are important for maintaining immune tolerance and resolution of inflammation, respectively. Cytokines trigger signaling pathways in naive T cells that induce lineage-defining transcription factors that direct their differentiation into the distinct T helper cell subsets. It has become clear that the differentiation of T helper cells is not only influenced by the cytokine milieu but also by their metabolic state, cues from the microbiota and the tissue they reside in. A comprehensive understanding how these various stimuli contribute to T helper cell differentiation and phenotype could potentially provide novel ways for therapeutic intervention in autoimmunity and tissue inflammation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
V.K.K. is cofounder of Celsius Therapeutics, Tizona Therapeutics and Bicara Therapeutics. His interests are reviewed and managed by the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Partners Healthcare in accordance with their conflict of interest policies.
Figures

References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL: Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol 1986, 136:2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, Sullivan BM, Peng SL, Glimcher LH: Molecular mechanisms regulating Th1 immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 2003, 21:713–758. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG, Glimcher LH: A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell 2000, 100:655–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

