Antibody dynamics to SARS-CoV-2 in asymptomatic COVID-19 infections
- PMID: 33040337
- PMCID: PMC7675426
- DOI: 10.1111/all.14622
Antibody dynamics to SARS-CoV-2 in asymptomatic COVID-19 infections
Abstract
Background: The missing asymptomatic COVID-19 infections have been overlooked because of the imperfect sensitivity of the nucleic acid testing (NAT). Globally understanding the humoral immunity in asymptomatic carriers will provide scientific knowledge for developing serological tests, improving early identification, and implementing more rational control strategies against the pandemic.
Measure: Utilizing both NAT and commercial kits for serum IgM and IgG antibodies, we extensively screened 11 766 epidemiologically suspected individuals on enrollment and 63 asymptomatic individuals were detected and recruited. Sixty-three healthy individuals and 51 mild patients without any preexisting conditions were set as controls. Serum IgM and IgG profiles were further probed using a SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray, and neutralizing antibody was detected by a pseudotyped virus neutralization assay system. The dynamics of antibodies were analyzed with exposure time or symptoms onset.
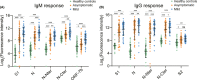
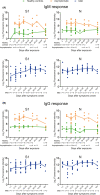
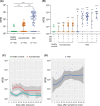
Results: A combination test of NAT and serological testing for IgM antibody discovered 55.5% of the total of 63 asymptomatic infections, which significantly raises the detection sensitivity when compared with the NAT alone (19%). Serum proteome microarray analysis demonstrated that asymptomatics mainly produced IgM and IgG antibodies against S1 and N proteins out of 20 proteins of SARS-CoV-2. Different from strong and persistent N-specific antibodies, S1-specific IgM responses, which evolved in asymptomatic individuals as early as the seventh day after exposure, peaked on days from 17 days to 25 days, and then disappeared in two months, might be used as an early diagnostic biomarker. 11.8% (6/51) mild patients and 38.1% (24/63) asymptomatic individuals did not produce neutralizing antibody. In particular, neutralizing antibody in asymptomatics gradually vanished in two months.
Conclusion: Our findings might have important implications for the definition of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections, diagnosis, serological survey, public health, and immunization strategies.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody dynamics; asymptomatic; neutralizing antibody.
© European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Dr Lei has nothing to disclose. Dr Li has nothing to disclose. Dr Hou has nothing to disclose. Dr Wang has nothing to disclose. Dr Ouyang has nothing to disclose. Dr Zhang has nothing to disclose. Dr Lai has nothing to disclose. Dr Banga Ndzouboukou has nothing to disclose. Dr Xu has nothing to disclose. Dr Zhang has nothing to disclose. Dr Chen has nothing to disclose. Dr Xue has nothing to disclose. Dr Lin has nothing to disclose. Dr Zheng has nothing to disclose. Dr Yao has nothing to disclose. Dr Wang has nothing to disclose. Dr Yu has nothing to disclose. Dr Jiang has nothing to disclose. Dr Zhang has nothing to disclose. Dr Qi has nothing to disclose. Dr Guo has nothing to disclose. Dr Huang has nothing to disclose. Dr Sun has nothing to disclose. Dr Tao has nothing to disclose. Dr Fan has nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- China Daily . WHO declares COVID‐19 a pandemic. Available at: http://www.nytimes.com/2020/03/11/world/coronavirus‐news.htm#link‐682e5b06. Accessed 21 June, 2020.
-
- WHO . Coronavirus disease (COVID‐2019) situation reports. Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel‐coronavirus‐2019/situatio.... Accessed 20 June, 2020.
-
- National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China . COVID‐19 Prevention and Control Plan, 3th edition. Available at: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020‐01/29/content_5472893.htm. Accessed June 22, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan J. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020;323:1239 ‐ 1242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016YFA0500600/National Key Research and Development Program of China Grant
- YG2020YQ10/Interdisciplinary Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University
- 2020kfyXGYJ040/HUST COVID-19 Rapid Response Call
- 2018ZX10302302002-001/National Mega-Projects of Science Research for the 13th Five-year Plan of China
- 2016YFA0500600/Research and Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

