A successfully treated case of primary purulent pericarditis complicated by cardiac tamponade and pneumopericardium
- PMID: 33040519
- PMCID: PMC7940096
- DOI: 10.4266/acc.2020.00234
A successfully treated case of primary purulent pericarditis complicated by cardiac tamponade and pneumopericardium
Abstract
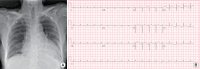
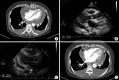
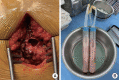
Acute pericarditis is caused by various factors, but purulent pericarditis is rare. Primary purulent pericarditis in immunocompetent hosts is very rare in the modern antibiotics era. We report a successfully treated case of primary purulent pericarditis complicated with cardiac tamponade and pneumopericardium in an immunocompetent host. A 69-year-old female was referred from another hospital because of pleuritic chest pain with a large amount of pericardial effusion. She was diagnosed with acute pericarditis accompanied by cardiac tamponade. We performed emergency pericardiocentesis, with drainage of 360 ml of bloody pericardial fluid. The culture grew Streptococcus anginosus, confirming the diagnosis of acute purulent pericarditis. We performed pericardiostomy because cardiomegaly and pneumopericardium were aggravated after removal of the pericardial drainage catheter. The patient received antibiotics for a total of 23 days intravenously and was discharged with oral antibiotic therapy. Purulent pericarditis is one of the rare forms of pericarditis and is lifethreatening. A multimodality approach is required for proper diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
Keywords: Cardiac tamponade; Pericardiocentesis; Pericarditis; Streptococcus anginosus.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Klacsmann PG, Bulkley BH, Hutchins GM. The changed spectrum of purulent pericarditis: an 86 year autopsy experience in 200 patients. Am J Med. 1977;63:666–73. - PubMed
-
- Parikh SV, Memon N, Echols M, Shah J, McGuire DK, Keeley EC. Purulent pericarditis: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2009;88:52–65. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources