Functions of dopamine in plants: a review
- PMID: 33040671
- PMCID: PMC7671028
- DOI: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1827782
Functions of dopamine in plants: a review
Abstract
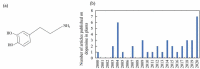
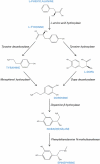
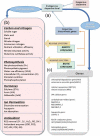
Dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine or 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) has many functions in animals, but also shows several other functions in plants. Since the discovery of dopamine in plants in 1968, many studies have provided insight into physiological and biochemical functions, and stress responses of this molecule. In this review, we describe the biosynthesis of dopamine, as well as its role in plant growth and development. In addition, endogenous or exogenously applied dopamine improved the tolerance against several abiotic stresses, such as drought, salt, and nutrient stress. There are also several studies that dopamine contributes to the plant immune response against plant disease. Dopamine affects the expression of many abiotic stresses related genes, which highlights its role as a multi-regulatory molecule and can coordinate many aspects of plant development. Our review emphasized the effects of dopamine against environmental stresses along with future research directions, which will help improve the yield of eco-friendly crops and ensure food security.
Keywords: 3,4- dihydroxy phenethylamine; abiotic stress; biosynthetic pathway; biotic stress; plant.
Figures
References
-
- Kulma A, Szopa J.. Catecholamines are active compounds in plants. Plant Sci. 2007;172(3):1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.10.013. - DOI
-
- Etienne AC, Peter JH, Andrea NB, Aparna S, Nicholas GC, Christine S, Thorvald FA, Ulrik G, Jeremy V, James SS, et al. Rare autism-associated variants implicate syntaxin 1 (STX1 R26Q) phosphorylation and the dopamine transporter (hDAT R51W) in dopamine neurotransmission and behaviors. EBioMedicine. 2015;2:135–146. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.01.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
