Synthetic Lethal Interactions of RECQ Helicases
- PMID: 33041245
- PMCID: PMC7855770
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.09.001
Synthetic Lethal Interactions of RECQ Helicases
Abstract
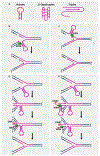
DNA helicases have risen to the forefront as genome caretakers. Their prominent roles in chromosomal stability are demonstrated by the linkage of mutations in helicase genes to hereditary disorders with defects in DNA repair, the replication stress response, and/or transcriptional activation. Conversely, accumulating evidence suggests that DNA helicases in cancer cells have a network of pathway interactions such that codeficiency of some helicases and their genetically interacting proteins results in synthetic lethality (SL). Such genetic interactions may potentially be exploited for cancer therapies. We discuss the roles of RECQ DNA helicases in cancer, emphasizing some of the more recent developments in SL.
Keywords: Bloom’s syndrome; RECQ; Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome; Werner syndrome; cancer; genetic disease; genomic stability; helicase; synthetic lethality.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

