COVID-19: Reduction of airborne transmission needs paradigm shift in ventilation
- PMID: 33041457
- PMCID: PMC7536125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.107336
COVID-19: Reduction of airborne transmission needs paradigm shift in ventilation
Figures
References
-
- Ai Z.T., Melikov A.K. Airborne spread of expiratory droplet nuclei between the occupants of indoor environments: a review article. Indoor Air. 2018;28(4):500–524. - PubMed
-
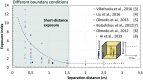
- Villafruela J.M., Olmedo I., San Jose J.F. Influence of human breathing modes on airborne cross infection risk. Build. Environ. 2016;106:340–351.
-
- Liu L., Li Y., Nielsen P.V. Short-range airborne transmission of expiratory droplets between two people. Indoor Air. 2016;27(2):452–462. - PubMed
-
- Olmedo I., Nielsen P.V., Ruiz de Adana M., Jensen R.L. The risk of airborne cross infection in a room with vertical low-velocity ventilation. Indoor Air. 2013;23:62–73. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
