Habitat suitability model of endangered Latidens salimalii and the probable consequences of global warming
- PMID: 33041475
- PMCID: PMC7539283
- DOI: 10.1007/s42965-020-00114-5
Habitat suitability model of endangered Latidens salimalii and the probable consequences of global warming
Abstract
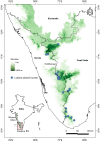
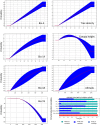
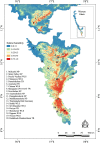
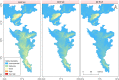
Salim Ali's fruit bat, Latidens salimalii, is a monotypic endangered fruit bat endemic to Western Ghats (WG) with an ambiguous distribution. The distribution range, habitat suitability, and biology of this species are still uncertain. Endemic species inhabiting the high elevation of WG like L. salimalii are threatened due to climatic change and seeks urgent management interventions. Hence, we developed a habitat suitability model for L. salimalii using MaxEnt in the current climate condition and projected their distribution for three Representation Concentration Pathway (RCP 4.5, 6.0, and 8.5) climate scenarios of the 2070 time frame. The results show that 9531 km2of habitat in WG is suitable for L. salimalii at present, while all the future scenarios estimates propose complete loss of highly suitable habitat. The significant factors influencing the distribution of L. salimalii are the precipitation of the driest month, tree density, rain in the coldest quarter, canopy height, and altitude. The study pioneers in predicting the suitable habitat and emphasis the need to develop strategies for the long-term conservation of endangered L. salimalii in WG under global warming scenarios.
Keywords: Climate change; Endemic species; Habitat loss; Maxent; Western Ghats.
© International Society for Tropical Ecology 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modeling the effect of climate change on the distribution of threatened medicinal orchid Satyrium nepalense D. Don in India.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Oct;29(48):72431-72444. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20412-w. Epub 2022 May 7. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35524848
-
Modeling the Current and Future Distribution of Indianthus virgatus (Roxb.) Suksathan & Borchs.: A Monotypic Plant Endemic to the Western Ghats-Sri Lanka Biodiversity Hotspot.Ecol Evol. 2024 Oct 26;14(10):e70489. doi: 10.1002/ece3.70489. eCollection 2024 Oct. Ecol Evol. 2024. PMID: 39463734 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of climate change on the nearly threatened taxa Elaeocarpus munroi (Wight) Mast. inhabiting in the forest of the Western Ghats.Environ Monit Assess. 2025 Jan 7;197(2):146. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13570-6. Environ Monit Assess. 2025. PMID: 39775267
-
Predicting the habitat suitability and species richness of plants of Great Himalayan National Park under different climate change scenarios.Environ Monit Assess. 2024 Oct 30;196(11):1136. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13290-x. Environ Monit Assess. 2024. PMID: 39477861
-
Effects of Climate Change on the Distribution of Threatened Fishing Bat Myotis pilosus in China.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 27;13(11):1784. doi: 10.3390/ani13111784. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37889742 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The devil is in the detail: Environmental variables frequently used for habitat suitability modeling lack information for forest-dwelling bats in Germany.Ecol Evol. 2024 Jun 26;14(6):e11571. doi: 10.1002/ece3.11571. eCollection 2024 Jun. Ecol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38932971 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting current and future habitat of Indian pangolin (Manis crassicaudata) under climate change.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 30;14(1):7564. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58173-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38555376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agoramoorthy G, Hsu M. Population size, feeding, forearm length, and bodyweight of a less known India fruit bat, Latidens salimalii. Curr Sci. 2005;88(3):354–356.
-
- Aiello-Lammens ME, Boria RA, Radosavljevic A, Vilela B, Anderson RP. spThin: An R package for spatial thinning of species occurrence records for use in ecological niche models. Ecography. 2015;38:541–545. doi: 10.1111/ecog.01132. - DOI
-
- Allouche O, Tsoare A, Kadmon R. Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS) J Appl Ecol. 2006;43:1223–1232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2664.2006.01214.x. - DOI
-
- Arasumani M, Khan D, Vishnudas CK, Muthukumar M, Milind B, Robin VV. Invasion compounds an ecosystem-wide loss to afforestation in the tropical grasslands of the Shola Sky Islands. Biol Conserv. 2019;230:141–150. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2018.12.019. - DOI
-
- Austin M. Species distribution models and ecological theory: a critical assessment and some possible new approaches. Ecol Modell. 2007;200:1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.07.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
