Current trends and prospects of tidal energy technology
- PMID: 33041645
- PMCID: PMC7538194
- DOI: 10.1007/s10668-020-01013-4
Current trends and prospects of tidal energy technology
Abstract
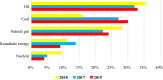
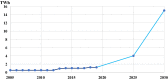
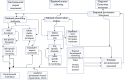
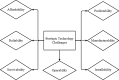
Generation of energy across the world is today reliant majorly on fossil fuels. The burning of these fuels is growing in line with the increase in the demand for energy globally. Consequently, climate change, air contamination, and energy security issues are rising as well. An efficient alternative to this grave hazard is the speedy substitution of fossil fuel-based carbon energy sources with the shift to clean sources of renewable energy that cause zero emissions. This needs to happen in conjunction with the continuing increase in the overall consumption of energy worldwide. Many resources of renewable energy are available. These include thermal, solar photovoltaic, biomass and wind, tidal energy, hydropower, and geothermal. Notably, tidal energy exhibits great potential with regard to its dependability, superior energy density, certainty, and durability. The energy mined from the tides on the basis of steady and anticipated vertical movements of the water, causing tidal currents, could be converted into kinetic energy to produce electricity. Tidal barrages could channel mechanical energy, while tidewater river turbines can seize the energy from tidal currents. This study discusses the present trends, ecological effects, and the prospects for technology related to tidal energy.
Keywords: Current trends; Environmental impact; Prospects; Tidal energy.
© Springer Nature B.V. 2020.
Figures

References
-
- Abiad, A. A., & Rosa Mia Dagli, S. (2020). The economic impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on developing Asia. Adrian 2020. Renewable Capacity Statistics 2020.
-
- April 10, 2014. OpenHydro to Build $833 Million Tidal-Power Plant in Alderney. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2014-04-10/openhydro-to-build-83....
-
- Badcock-Broe, A., Flynn, R., George, S., Gruet, R., & Medic, N. (2014). Wave and tidal energy market deployment strategy for Europe. In Strategic Initiative for Ocean Energy (SI Ocean).http://www.si-ocean.eu/en/Market-Deployment/MarketDeployment-Strategy.
-
- Barrier, E. S. S. S. (2016). Eastern Scheldt storm surge barrier. https://www.dutchwatersector.com/news/tocardo-to-place-tidal-energy-turb....
-
- BBC. India plans Asian tidal power first. BBC.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
