Levofloxacin for Antibacterial Prophylaxis in Pediatric Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia or Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- PMID: 33041718
- PMCID: PMC7541028
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-25.7.629
Levofloxacin for Antibacterial Prophylaxis in Pediatric Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia or Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the use of levofloxacin for the prevention of bacterial infections in pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia or those undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Methods: This study was a single-center, retrospective review designed to assess the frequency of bacteremia with levofloxacin prophylaxis compared with historical controls that used other, clinician-directed antibacterial prophylaxis. The primary outcome of the study was microbiologically documented bacteremia. Secondary outcomes included febrile neutropenia, clinically documented infection, duration of neutropenia, treatment antibiotic exposure days, Clostridioides difficile infection, and infection-related mortality.
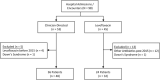
Results: Of the 60 patients included, 24 patients with 32 hospital admissions received levofloxacin and 36 patients with 48 hospital admissions received clinician-directed prophylaxis. There was no difference found in the frequency of bacteremia between levofloxacin and clinician-directed prophylaxis (15.6% vs 10.4%, p = 0.49). There was no difference in the incidence of febrile neutropenia, clinically documented infection, treatment antibiotic exposure days, or 30-day infection-related mortality between the 2 groups. The levofloxacin group had a longer mean duration of neutropenia compared with clinician-directed prophylaxis (26.8 days vs 16.4 days, p = 0.01).
Conclusions: There was no difference in bacteremia between levofloxacin prophylaxis and clinician-directed prophylaxis in pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia or those undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Levofloxacin prophylaxis is an appropriate alternative for the prevention of serious bacterial infections in this patient population, although further studies are needed to confirm these results.
Keywords: antibacterial prophylaxis; infection; leukemia; levofloxacin; pediatric; stem cell transplant.
Copyright Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, email: mhelms@pediatricpharmacy.org 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors declare no conflicts or financial interest in any product or service mentioned in the manuscript, including grants, equipment, medications, employment, gifts, and honoraria. The authors had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Similar articles
-
Effect of Levofloxacin Prophylaxis on Bacteremia in Children With Acute Leukemia or Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2018 Sep 11;320(10):995-1004. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.12512. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 30208456 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Prophylactic Levofloxacin in Pediatric and Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Patients.Transplant Cell Ther. 2022 Mar;28(3):167.e1-167.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2021.11.017. Epub 2021 Dec 4. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022. PMID: 34875405
-
Levofloxacin Prophylaxis During Induction Therapy for Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Nov 13;65(11):1790-1798. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix644. Clin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29020310 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of levofloxacin as an antibacterial prophylaxis for acute leukemia patients receiving intensive chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hematology. 2019 Dec;24(1):362-368. doi: 10.1080/16078454.2019.1589706. Hematology. 2019. PMID: 30880638
-
Guideline for Antibacterial Prophylaxis Administration in Pediatric Cancer and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Jun 24;71(1):226-236. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz1082. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31676904 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of levofloxacin in the induction of chemotherapy in high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children in a developing country.Ecancermedicalscience. 2023 Sep 25;17:1606. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2023.1606. eCollection 2023. Ecancermedicalscience. 2023. PMID: 37799940 Free PMC article.
-
Levofloxacin Versus Ciprofloxacin-Based Prophylaxis during the Pre-Engraftment Phase in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Pediatric Recipients: A Single-Center Retrospective Matched Analysis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Dec 14;10(12):1523. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121523. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943735 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of infections in different regimens of post-induction chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia (de-novo): A comparative retrospective study.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 17;10(3):e24561. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24561. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38317981 Free PMC article.
-
Lactoferricin B Combined with Antibiotics Exhibits Leukemic Selectivity and Antimicrobial Activity.Molecules. 2024 Feb 1;29(3):678. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030678. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cecinati V, Principi N, Brescia L, Esposito S. Antibiotic prophylaxis in children with cancer or who have undergone hematopoietic cell transplantation. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;33(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Choeyprasert W, Hongeng S, Anurathapan U, Pakakasama S. Bacteremia during neutropenic episodes in children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with ciprofloxacin and penicillin prophylaxis. Int J Hematol. 2017;105(2):213–220. - PubMed
-
- Sung L, Lange BJ, Gerbing RB et al. Microbiologically documented infections and infection-related mortality in children with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2007;110(10):3532–3539. - PubMed
-
- Lehrnbecher T, Sung L. Anti-infective prophylaxis in pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev Hematol. 2014;7(6):819–830. - PubMed
-
- Freifeld AG, Bow EJ, Sepkowitz KA et al. Clinical practice guideline for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer: 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(4):56–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources