Potential Therapeutic Options for COVID-19: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 33041814
- PMCID: PMC7522523
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.572870
Potential Therapeutic Options for COVID-19: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
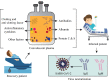
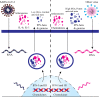
The COVID-19 pandemic represents an unprecedented challenge for the researchers to offer safe, tolerable, and effective treatment strategies for its causative agent known as SARS-CoV-2. With the rapid evolution of the pandemic, even the off-label use of existing drugs has been restricted by limited availability. Several old antivirals, antimalarial, and biological drugs are being reconsidered as possible therapies. The effectiveness of the controversial treatment options for COVID-19 such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, angiotensin 2 conversion enzyme inhibitors and selective angiotensin receptor blockers was also discussed. A systemic search in the PubMed, Science Direct, LitCovid, Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, and ClinicalTrials.gov data bases was conducted using the keywords "coronavirus drug therapy," passive immunotherapy for COVID-19', "convalescent plasma therapy," (CPT) "drugs for COVID-19 treatment," "SARS-CoV-2," "COVID-19," "2019-nCoV," "coronavirus immunology," "microbiology," "virology," and individual drug names. Systematic reviews, case presentations and very recent clinical guidelines were included. This narrative review summarizes the available information on possible therapies for COVID-19, providing recent data to health professionals.
Keywords: COVID-19 proposed therapy; Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2); convalescent plasma; pandemic; therapeutic challenges.
Copyright © 2020 Sarkar, Mondal, Torequl Islam, Martorell, Docea, Maroyi, Sharifi-Rad and Calina.
Figures


References
-
- (WHO), W.H.O (2020). WHO welcomes preliminary results about dexamethasone use in treating critically ill COVID-19 patients. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/16-06-2020-who-welcomes-preliminary... Accesed on July 23, 2020.
-
- Agency E. M. (2020). Veklury. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/veklury (Accesed on July 30, 2020).
-
- Al-Saikhan F. I., Al-Shdefat R. I., Abd-Elaziz M. A., Adam E. H. K., Ahsan F. (2015). Development and Validation of RP-HPLC Method for Quantitation of Aviptadil Acetate and its Degradation Products. Asian J. Biol. Life Sci. 4 1, 76–80.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

