The Potential Role of SARS-COV-2 in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 33041985
- PMCID: PMC7527541
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.01044
The Potential Role of SARS-COV-2 in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
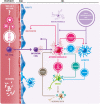
Considering their current burden and epidemiological projections, nowadays Parkinson's disease and the COVID-19 pandemic are two key health problems. There is evidence of the pathogenic role of neurotropic viruses in neurodegenerative diseases and coronaviruses are neurotropic, with some of them selectively targeting the basal ganglia. Moreover, some authors demonstrated the longevity of these viruses in the affected cells of the nervous system for long periods. Coronavirus was detected in brain autopsies and SARS-CoV-2 has been isolated from the CSF of affected patients. The marked inflammatory response in some particular patients with COVID-19 with a consequent increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines is considered a prognostic factor. Immunologic changes are observed in patients with Parkinson's disease, possibly having a role in its pathogenesis. A dynamic pro-inflammatory state accompanies α-synuclein accumulation and the development and progression of neurodegeneration. Also, some viral infectious diseases might have a role as triggers, generating a cross autoimmune reaction against α-synuclein. In the past Coronaviruses have been related to Parkinson's disease, however, until now the causal role of these viruses is unknown. In this paper, our focus is to assess the potential relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Parkinson disease; SARS virus; alpha-synuclein; coronavirus; movement disorders; nervous system diseases; neurodegenerative diseases; pandemics.
Copyright © 2020 Chaná-Cuevas, Salles-Gándara, Rojas-Fernandez, Salinas-Rebolledo and Milán-Solé.
Figures
References
-
- Ray Dorsey E, Elbaz A, Nichols E, Abd-Allah F, Abdelalim A, Adsuar JC, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson's disease, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol. (2018) 17:939–53. 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30499-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

