Maternal High Fat Diet and Diabetes Disrupts Transcriptomic Pathways That Regulate Cardiac Metabolism and Cell Fate in Newborn Rat Hearts
- PMID: 33042024
- PMCID: PMC7527411
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.570846
Maternal High Fat Diet and Diabetes Disrupts Transcriptomic Pathways That Regulate Cardiac Metabolism and Cell Fate in Newborn Rat Hearts
Abstract
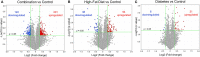
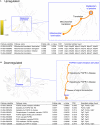
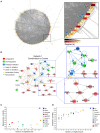
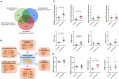
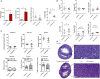
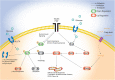
Background: Children born to diabetic or obese mothers have a higher risk of heart disease at birth and later in life. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, we previously demonstrated that late-gestation diabetes, maternal high fat (HF) diet, and the combination causes distinct fuel-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of rat cardiac tissue during fetal cardiogenesis. The objective of the present study was to investigate the overall transcriptional signature of newborn offspring exposed to maternal diabetes and maternal H diet. Methods: Microarray gene expression profiling of hearts from diabetes exposed, HF diet exposed, and combination exposed newborn rats was compared to controls. Functional annotation, pathway and network analysis of differentially expressed genes were performed in combination exposed and control newborn rat hearts. Further downstream metabolic assessments included measurement of total and phosphorylated AKT2 and GSK3β, as well as quantification of glycolytic capacity by extracellular flux analysis and glycogen staining. Results: Transcriptional analysis identified significant fuel-mediated changes in offspring cardiac gene expression. Specifically, functional pathways analysis identified two key signaling cascades that were functionally prioritized in combination exposed offspring hearts: (1) downregulation of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) activated PI3K/AKT pathway and (2) upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator alpha (PGC1α) mitochondrial biogenesis signaling. Functional metabolic and histochemical assays supported these transcriptome changes, corroborating diabetes- and diet-induced cardiac transcriptome remodeling and cardiac metabolism in offspring. Conclusion: This study provides the first data accounting for the compounding effects of maternal hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia on the developmental cardiac transcriptome, and elucidates nuanced and novel features of maternal diabetes and diet on regulation of heart health.
Keywords: PI3K/Akt pathway; cardiovascular disease; functional genomics; high fat diet; maternal diabetes; mitochondrial biogenesis.
Copyright © 2020 Preston, Larsen, Eclov, Louwagie, Gandy, Faustino and Baack.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Consequences of a Maternal High-Fat Diet and Late Gestation Diabetes on the Developing Rat Lung.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 12;11(8):e0160818. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160818. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27518105 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal high-fat diet impairs cardiac function in offspring of diabetic pregnancy through metabolic stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Mar 15;310(6):H681-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00795.2015. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26801311 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Exposure to a Maternal High-Fat Diet Affects Histone Modification of Cardiometabolic Genes in Newborn Rats.Nutrients. 2017 Apr 20;9(4):407. doi: 10.3390/nu9040407. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28425976 Free PMC article.
-
High Fat Programming and Cardiovascular Disease.Medicina (Kaunas). 2018 Nov 13;54(5):86. doi: 10.3390/medicina54050086. Medicina (Kaunas). 2018. PMID: 30428585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consensus Transcriptional Landscape of Human End-Stage Heart Failure.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Apr 6;10(7):e019667. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019667. Epub 2021 Mar 31. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33787284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal obesity programs cardiac remodeling in offspring via epigenetic, metabolic, and immune dysregulations.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 27:2025.04.15.648971. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.15.648971. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40502137 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Maternal High-Fat Diet and Offspring Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 25;23(15):8179. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158179. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrauterine Programming of Cardiovascular Diseases in Maternal Diabetes.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 3;12:760251. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.760251. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34803741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal High-Fat Diet Controls Offspring Kidney Health and Disease.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 9;15(12):2698. doi: 10.3390/nu15122698. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37375602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal Nutritional Programming: Sex-Specific Cardiovascular and Immune Outcomes Following Perinatal High-Fat Diet Exposure.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 26;17(9):1464. doi: 10.3390/nu17091464. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362773 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

