Postnatal Expansion, Maturation, and Functionality of MR1T Cells in Humans
- PMID: 33042140
- PMCID: PMC7524872
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.556695
Postnatal Expansion, Maturation, and Functionality of MR1T Cells in Humans
Abstract
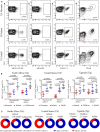
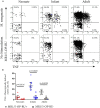
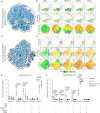
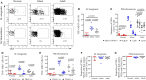
MR1-restricted T (MR1T) cells are defined by their recognition of metabolite antigens presented by the monomorphic MHC class 1-related molecule, MR1, the most highly conserved MHC class I related molecule in mammalian species. Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are the predominant subset of MR1T cells expressing an invariant TCR α-chain, TRAV1-2. These cells comprise a T cell subset that recognizes and mediates host immune responses to a broad array of microbial pathogens, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Here, we sought to characterize development of circulating human MR1T cells as defined by MR1-5-OP-RU tetramer labeling and of the TRAV1-2+ MAIT cells defined by expression of TRAV1-2 and high expression of CD26 and CD161 (TRAV1-2+CD161++CD26++ cells). We analyzed postnatal expansion, maturation, and functionality of peripheral blood MR1-5-OP-RU tetramer+ MR1T cells in cohorts from three different geographic settings with different tuberculosis (TB) vaccination practices, levels of exposure to and infection with M. tuberculosis. Early after birth, frequencies of MR1-5-OP-RU tetramer+ MR1T cells increased rapidly by several fold. This coincided with the transition from a predominantly CD4+ and TRAV1-2- population in neonates, to a predominantly TRAV1-2+CD161++CD26++ CD8+ population. We also observed that tetramer+ MR1T cells that expressed TNF upon mycobacterial stimulation were very low in neonates, but increased ~10-fold in the first year of life. These functional MR1T cells in all age groups were MR1-5-OP-RU tetramer+TRAV1-2+ and highly expressed CD161 and CD26, markers that appeared to signal phenotypic and functional maturation of this cell subset. This age-associated maturation was also marked by the loss of naïve T cell markers on tetramer+ TRAV1-2+ MR1T cells more rapidly than tetramer+TRAV1-2- MR1T cells and non-MR1T cells. These data suggest that neonates have infrequent populations of MR1T cells with diverse phenotypic attributes; and that exposure to the environment rapidly and preferentially expands the MR1-5-OP-RU tetramer+TRAV1-2+ population of MR1T cells, which becomes the predominant population of functional MR1T cells early during childhood.
Keywords: MAIT cells; human mucosal immunology; infant; innate T cells; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2020 Swarbrick, Gela, Cansler, Null, Duncan, Nemes, Shey, Nsereko, Mayanja-Kizza, Kiguli, Koh, Hanekom, Hatherill, Lancioni, Lewinsohn, Scriba and Lewinsohn.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Neonatal MR1T Cells Have Diverse TCR Usage, are Less Cytotoxic and are Unable to Respond to Many Common Childhood Pathogens.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 18:2025.03.17.643805. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.17.643805. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40166301 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Human Neonatal MR1T Cells Have Diverse TCR Usage, are Less Cytotoxic and are Unable to Respond to Many Common Childhood Pathogens.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 1:rs.3.rs-6265058. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6265058/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 40235492 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Dual TCR-α Expression on Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells as a Potential Confounder of TCR Interpretation.J Immunol. 2022 Mar 15;208(6):1389-1395. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100275. Epub 2022 Mar 4. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35246495 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen Recognition by MR1-Reactive T Cells; MAIT Cells, Metabolites, and Remaining Mysteries.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 27;11:1961. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01961. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MR1-Restricted T Cells Are Unprecedented Cancer Fighters.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 28;11:751. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00751. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32411144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Skewing of Circulating MR1-Restricted and γδ T Cells in Human Psoriasis Vulgaris.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 3;11:572924. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.572924. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33343564 Free PMC article.
-
Human Neonatal MR1T Cells Have Diverse TCR Usage, are Less Cytotoxic and are Unable to Respond to Many Common Childhood Pathogens.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 18:2025.03.17.643805. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.17.643805. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40166301 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
MAIT cells numbers and frequencies in patients with acute myeloid leukemia at diagnosis: association with cytogenetic profile and gene mutations.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022 Apr;71(4):875-887. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03037-9. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022. PMID: 34477901 Free PMC article.
-
T cell receptor diversity, specificity and promiscuity of functionally heterogeneous human MR1-restricted T cells.Mol Immunol. 2021 Feb;130:64-68. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.12.009. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33360378 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells and innate lymphoid cells but not NKT cells are mature in their cytokine production at birth.Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Jan 9;215(1):1-14. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad094. Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37556759 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

