SYTL4 downregulates microtubule stability and confers paclitaxel resistance in triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 33042263
- PMCID: PMC7532662
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.45207
SYTL4 downregulates microtubule stability and confers paclitaxel resistance in triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
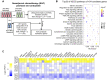
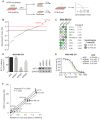
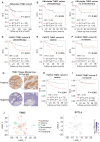
Background: Taxanes are frontline chemotherapeutic drugs for patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC); however, chemoresistance reduces their effectiveness. We hypothesized that the molecular profiling of tumor samples before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) would help identify genes associated with drug resistance. Methods: We sequenced 10 samples by RNA-seq from 8 NAC patients with TNBC: 3 patients with a pathologic complete response (pCR) and the other 5 with non-pCR. Differentially expressed genes that predicted chemotherapy response were selected for in vitro functional screening via a small-scale siRNAs pool. The clinical and functional significance of the gene of interest in TNBC was further investigated in vitro and in vivo, and biochemical assays and imaging analysis were applied to study the mechanisms. Results: Synaptotagmin-like 4 (SYTL4), a Rab effector in vesicle transport, was identified as a leading functional candidate. High SYTL4 expression indicated a poor prognosis in multiple TNBC cohorts, specifically in taxane-treated TNBCs. SYTL4 was identified as a novel chemoresistant gene as validated in TNBC cells, a mouse model and patient-derived organoids. Mechanistically, downregulating SYTL4 stabilized the microtubule network and slowed down microtubule growth rate. Furthermore, SYTL4 colocalized with microtubules and interacted with microtubules through its middle region containing the linker and C2A domain. Finally, we found that SYTL4 was able to bind microtubules and inhibit the in vitro microtubule polymerization. Conclusion: SYTL4 is a novel chemoresistant gene in TNBC and its upregulation indicates poor prognosis in taxane-treated TNBC. Further, SYTL4 directly binds microtubules and decreases microtubule stability.
Keywords: SYTL4; Triple-negative breast cancer; microtubule polymerization; paclitaxel resistance.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
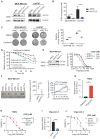
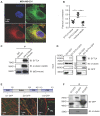

 . The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent assays (one-way ANOVA test, right panel). (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of microtubule stability in MDA-MB-231 cells at 0 °C and 37 °C (left). Tubule-like structures were recognized by Fiji using the Tubeness plugin (middle) as described in methods. The percentage (%) of polymerized microtubules was calculated by dividing the area of tubule-like structure into the region inside the cell contour (right) (mean ± SD, n = 20, one-way ANOVA test). * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; n.s: not significant.
. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent assays (one-way ANOVA test, right panel). (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of microtubule stability in MDA-MB-231 cells at 0 °C and 37 °C (left). Tubule-like structures were recognized by Fiji using the Tubeness plugin (middle) as described in methods. The percentage (%) of polymerized microtubules was calculated by dividing the area of tubule-like structure into the region inside the cell contour (right) (mean ± SD, n = 20, one-way ANOVA test). * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; n.s: not significant.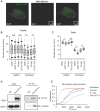
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F. et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:2329–2334. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS. Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1938–1948. - PubMed
-
- Jiang YZ, Ma D, Suo C, Shi J, Xue M, Hu X. et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers: Subtypes and Treatment Strategies. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:428–440. e425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

