Toll-like receptor 5 deficiency diminishes doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity in mice
- PMID: 33042267
- PMCID: PMC7532690
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.47516
Toll-like receptor 5 deficiency diminishes doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity in mice
Abstract
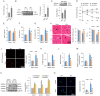
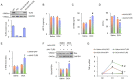
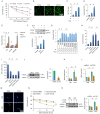
Rationale: Clinical application of doxorubicin (DOX) is limited by its toxic cardiovascular side effects. Our previous study found that toll-like receptor (TLR) 5 deficiency attenuated cardiac fibrosis in mice. However, the role of TLR5 in DOX-induced cardiotoxicity remains unclear. Methods: To further investigate this, TLR5-deficient mice were subjected to a single intraperitoneal injection of DOX to mimic an acute model. Results: Here, we reported that TLR5 expression was markedly increased in response to DOX injection. Moreover, TLR5 deficiency exerted potent protective effects against DOX-related cardiac injury, whereas activation of TLR5 by flagellin exacerbated DOX injection-induced cardiotoxicity. Mechanistically, the effects of TLR5 were largely attributed to direct interaction with spleen tyrosine kinase to activate NADPH oxidase (NOX) 2, increasing the production of superoxide and subsequent activation of p38. The toxic effects of TLR5 activation in DOX-related acute cardiac injury were abolished by NOX2 deficiency in mice. Our further study showed that neutralizing antibody-mediated TLR5 depletion also attenuated DOX-induced acute cardiotoxicity. Conclusion: These findings suggest that TLR5 deficiency attenuates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in mice, and targeting TLR5 may provide feasible therapies for DOX-induced acute cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: Apoptosis; NOX2; TLR5; cardiotoxicity; doxorubicin.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Carvalho FS, Burgeiro A, Garcia R, Moreno AJ, Carvalho RA, Oliveira PJ. Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: from bioenergetic failure and cell death to cardiomyopathy. Med Res Rev. 2014;34:106–35. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho RA, Sousa RP, Cadete VJ, Lopaschuk GD, Palmeira CM, Bjork JA. et al. Metabolic remodeling associated with subchronic doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Toxicology. 2010;270:92–8. - PubMed
-
- Lefrak EA, Pitha J, Rosenheim S, Gottlieb JA. A clinicopathologic analysis of adriamycin cardiotoxicity. Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. 1973;32:302–14. - PubMed
-
- Ibrahim NK, Hortobagyi GN, Ewer M, Ali MK, Asmar L, Theriault RL. et al. Doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure in elderly patients with metastatic breast cancer, with long-term follow-up: the M.D. Anderson experience. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43:471–8. - PubMed
-
- Von Hoff DD, Layard MW, Basa P, Davis HJ, Von Hoff AL, Rozencweig M. et al. Risk factors for doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure. Ann Intern Med. 1979;91:710–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

