The History of Hepatitis A
- PMID: 33042523
- PMCID: PMC7538924
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.1018
The History of Hepatitis A
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2021 Feb 28;17(2):97. doi: 10.1002/cld.1073. eCollection 2021 Feb. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 33680446 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Watch an interview with the author.
© 2020 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures




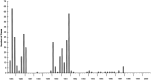
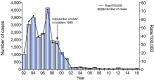
Similar articles
-
We Are All Africans: A Highly Personal Migratory View of the History of Hepatitis B.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020 Oct 7;16(Suppl 1):24-33. doi: 10.1002/cld.989. eCollection 2020 Oct. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 33042524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AGA Clinical Practice Update on Interaction Between Oral Direct-Acting Antivirals for Chronic Hepatitis C Infection and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Expert Review.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020 Jun 30;15(6):211-212. doi: 10.1002/cld.943. eCollection 2020 Jun. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 32617150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State of the Hepatitis C Virus Care Cascade.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020 Jul 21;16(1):8-11. doi: 10.1002/cld.915. eCollection 2020 Jul. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 32714516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Hepatitis C-Infected Patients After Sustained Virological Response.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020 Jul 21;16(1):20-24. doi: 10.1002/cld.913. eCollection 2020 Jul. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 32714519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Colocalization in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Care: The Role of Opioid Agonist Therapy Clinics.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020 Jul 21;16(1):12-15. doi: 10.1002/cld.921. eCollection 2020 Jul. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 32714517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The liver in Judaism.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2024 Jun 25;23(1):e0234. doi: 10.1097/CLD.0000000000000234. eCollection 2024 Jan-Jun. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38919868 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A History of the Assessment of Liver Performance.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2021 Oct 29;18(Suppl 1):28-48. doi: 10.1002/cld.1100. eCollection 2021 Oct. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 34745582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attitudes and Knowledge of European Medical Students and Early Graduates about Vaccination and Self-Reported Vaccination Coverage-Multinational Cross-Sectional Survey.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 30;18(7):3595. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073595. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33808446 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Technological Developments on Infectious Disease Epidemiology: Lessons From the First 100 Years of the American Journal of Epidemiology.Am J Epidemiol. 2023 Nov 3;192(11):1820-1826. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwac064. Am J Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 35362021 Free PMC article.
-
Male-Dominant Hepatitis A Outbreak Observed among Non-HIV-Infected Persons in the Northern Part of Tokyo, Japan.Viruses. 2021 Jan 29;13(2):207. doi: 10.3390/v13020207. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33573054 Free PMC article.
References
-
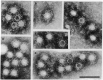
- Feinstone S, Kapikian AZ, Purcell RH. Hepatitis A: detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science 1973;182:1026‐1028. - PubMed
-
- Zuckerman AJ. The history of viral hepatitis from antiquity to the present In: Deinhardt F, Deinhardt J, eds. Viral Hepatitis. Laboratory and Clinical Science. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1983:3‐34.
-
- Kulkarni MA, Walimbe AM, Cherian S, et al. Full length genomes of genotype IIIA Hepatitis A Virus strains (1995‐2008) from India and estimates of the evolutionary rates and ages. Infect Genet Evol 2009;9:1287‐1294. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

