ASK1 inhibits proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells via inactivating TAZ
- PMID: 33042617
- PMCID: PMC7539782
ASK1 inhibits proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells via inactivating TAZ
Abstract
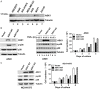
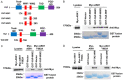
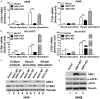
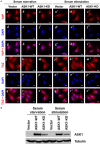
ASK1 (Apoptosis Signal-regulating Kinase 1, also MEKK5) is known to mediate cellular stress signaling pathways through activating p38 kinase. We here observed that ectopically expression of ASK1, but not its kinase-dead mutant, impaired cell proliferation and migration in lung cancer A549 and NCI-H1975 cells. To our surprise, this inhibitory effect of ASK1 is independent on activation of p38 kinase. We further discovered that ASK1 interacts with the WW domain of YAP and TAZ (also WWTR1) that are transcriptional co-activators and the Hippo signaling effectors. Overexpression of wild type ASK1, but not the kinase-dead mutant, in the lung cancer cells down-regulated the expression of the YAP/TAZ target genes CYR61 and CTGF. It seems that ASK1 specifically inactivates TAZ, not YAP, as ASK1 blocked nuclear translocation of TAZ only, while had no effect on YAP. Furthermore, knockdown of TAZ in the lung cancer cells caused the same inhibitory effect on cell proliferation and migration as that of overexpression of ASK1. Thus, our studies have defined a new signaling pathway of ASK1 for regulation of lung cancer cell proliferation and migration via interacting with and inactivating TAZ.
Keywords: ASK1; TAZ; lung cancer; migration; proliferation.
AJCR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distinctive Roles of YAP and TAZ in Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells Growth and Functions.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 11;10(1):147. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010147. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35052826 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Hippo Signaling Pathway for Tissue Regeneration and Cancer Therapy.Genes (Basel). 2016 Aug 30;7(9):55. doi: 10.3390/genes7090055. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27589805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAZ promotes cell growth and inhibits Celastrol-induced cell apoptosis.Biosci Rep. 2016 Sep 29;36(5):e00386. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160135. Print 2016 Oct. Biosci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27515420 Free PMC article.
-
YAP/TAZ: a promising target for squamous cell carcinoma treatment.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Jul 8;11:6245-6252. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S197921. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31360073 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo signaling pathway provides novel anti-cancer drug targets.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):16084-16098. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14306. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28035075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR56 Is an Inhibitory Checkpoint for NK Cell Migration.J Immunol. 2024 Nov 1;213(9):1349-1357. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2400228. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39320215 Free PMC article.
-
Non-hippo kinases: indispensable roles in YAP/TAZ signaling and implications in cancer therapy.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 May;50(5):4565-4578. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08329-0. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36877351 Review.
-
Insights into the post-translational modification and its emerging role in shaping the tumor microenvironment.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Dec 20;6(1):422. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00825-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34924561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Hippo Pathway in Prostate Cancer: What's New?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 4;13(4):611. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040611. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33557087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of WWOX Function in Modulating Cellular Pathways Activated by AP-2α and AP-2γ Transcription Factors in Bladder Cancer.Cells. 2022 Apr 19;11(9):1382. doi: 10.3390/cells11091382. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, ten Dijke P, Saitoh M, Moriguchi T, Takagi M, Matsumoto K, Miyazono K, Gotoh Y. Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science. 1997;275:90–4. - PubMed
-
- Matsukawa J, Matsuzawa A, Takeda K, Ichijo H. The ASK1-MAP kinase cascades in mammalian stress response. J Biochem. 2004;136:261–5. - PubMed
-
- Shiizaki S, Naguro I, Ichijo H. Activation mechanisms of ASK1 in response to various stresses and its significance in intracellular signaling. Adv Biol Regul. 2013;53:135–44. - PubMed
-
- Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H. Molecular mechanisms of the decision between life and death: regulation of apoptosis by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. J Biochem. 2001;130:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Dyari HRE, Rawling T, Chen Y, Sudarmana W, Bourget K, Dwyer JM, Allison SE, Murray M. A novel synthetic analogue of ω-3 17,18-epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid activates TNF receptor-1/ASK1/JNK signaling to promote apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. FASEB J. 2017;31:5246–5257. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
