Combined Plating of Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fractures, a Consecutive Series of 74 Cases
- PMID: 33042641
- PMCID: PMC7540645
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1712503
Combined Plating of Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fractures, a Consecutive Series of 74 Cases
Abstract
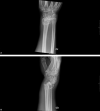
Background The distal radius fracture (DRF) is the most common fracture in adults. For unstable intra-articular fractures, the choice of treatment is often operative. The optimal choice of fixation remains a matter of discussion. Question/Purpose Can combined volar and dorsal plating, using a dorsal frame plate, achieve a good functional and radiographic 1-year outcome in intra-articular DRFs? Methods In a retrospective cohort study, we evaluated 74 consecutive patients operated with combined plating using a volar plate and a dorsal frame plate. The DRFs were operated between 2016 and 2017 and all cases were AO type C intra-articular fractures. The primary outcome was patient-reported outcome measures including radiographic examination 1 year postoperatively. Secondary outcome measures included wrist range of motion, visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, and hand grip strength. Results The median patient-rated wrist evaluation score was 18 points; the quick disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand score was 14.8 points. The median Batra radiographic score was 88. Wrist extension was 76% of the uninjured side, flexion was 74%, pronation was 94%, and supination was 94%. VAS pain scores were 0 at rest and 2 during activity. Hand grip strength was 82% compared with the uninjured side. The radiographic outcome according to Batra did not correspond to the patient-reported outcome. Patients older than 60 years had significantly better QuickDASH (quick disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand) and PRWE scores (patient-rated wrist evaluation scores) and less pain during activity compared with younger patients despite similar radiographic outcome. There were no tendon ruptures; hardware removal was performed in 21 of the 74 patients. Conclusion The radiographic outcome did not correspond to the functional outcome 1 year postoperatively. Older patients report less pain and better functional outcome compared with younger patients. There were no tendon ruptures and the frequency of hardware removal was acceptable. Complex intra-articular DRFs AO type C can be managed with volar and dorsal frame-plate fixation to restore distal radius anatomy and achieve a good functional outcome.
Keywords: distal radius fracture; plating; range of motion; visual analog scale.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Court-Brown C M, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006;37(08):691–697. - PubMed
-
- Handoll H H, Madhok R. Conservative interventions for treating distal radial fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(02):CD000314. - PubMed
-
- Handoll H H, Madhok R. Surgical interventions for treating distal radial fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(03):CD003209. - PubMed
-
- Mattila V M, Huttunen T T, Sillanpää P, Niemi S, Pihlajamäki H, Kannus P.Significant change in the surgical treatment of distal radius fractures: a nationwide study between 1998 and 2008 in Finland J Trauma 20117104939–942., discussion 942–943 - PubMed