Outcomes of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation With and Without Systemic Chemotherapy in Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33042792
- PMCID: PMC7525017
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01461
Outcomes of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation With and Without Systemic Chemotherapy in Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
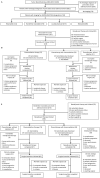
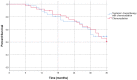
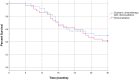
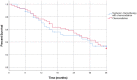
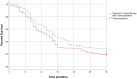
Introduction: Neoadjuvant therapy is increasingly being used for localized pancreatic adenocarcinoma. While there is evidence supporting neoadjuvant systemic chemotherapy as well as chemoradiation, more evidence is needed to determine whether systemic chemotherapy with chemoradiation offers benefits over chemoradiation alone. This study compares the outcomes of neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy with and without systemic chemotherapy in resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancers. Methods: This retrospective study evaluated patients with resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma who completed neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy with and without systemic chemotherapy prior to surgical resection. 149 patients met inclusion criteria, with 75 having resectable cancer and 74 having borderline resectable cancer. Outcomes included recurrence free and overall survival rates at 6, 12, and 36 months. Results: In resectable pancreatic carcinoma, 72% of patients treated with chemoradiation alone achieved 1 year recurrence free survival compared to 78% of patients treated with systemic chemotherapy and chemoradiation (p = 0.55). 28% of patients treated with chemoradiation alone had 3 years recurrence free survival compared to 31% of patients who received systemic and chemoradiation therapy (p = 0.75). In both treatment groups, 92% of patients lived past 1 year (p = 0.92), and 44% of patients survived at least 3 years (p = 0.95). In borderline resectable pancreatic carcinoma, 50% of patients treated with chemoradiation alone achieved 1 year recurrence free survival compared to 70% of patients treated with systemic chemotherapy and chemoradiation (p = 0.079). The 3 years recurrence free survival was 26 and 29% for the chemoradiation alone group and the systemic chemotherapy plus chemoradiation group, respectively (p = 0.85). There was no significant difference in 1 year overall survival: 85% of patients treated with chemoradiation alone survived compared to 92% of patients treated with systemic chemotherapy and chemoradiation (p = 0.32). Both groups had 41% 3 years overall survival (p = 0.96). Discussion: In resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma, there was no significant difference in overall or recurrence free survival between patients treated with chemoradiation with and without systemic chemotherapy. Our findings suggest that systemic neoadjuvant chemotherapy with chemoradiation and chemoradiation alone are efficacious treatments for localized pancreatic carcinoma. This brings into question whether more effective systemic chemotherapy is necessary to increase survival benefit.
Keywords: borderline resectable; chemoradiation (CRT); neoadjuavant chemotherapy; pancreas—adenocarcinoma; pancreatic cancer; systemic chemotherapy.
Copyright © 2020 Trinh, Fischer, Gardner and Smith.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postoperative complications after resection of borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer: The impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with conventional radiation or stereotactic body radiation therapy.Surgery. 2018 May;163(5):1090-1096. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.11.027. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Surgery. 2018. PMID: 29395234 Free PMC article.
-
Radiographic patterns of first disease recurrence after neoadjuvant therapy and surgery for patients with resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer.Surgery. 2020 Sep;168(3):440-447. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2020.04.031. Epub 2020 Jul 5. Surgery. 2020. PMID: 32641278
-
Long-term survival benefit of upfront chemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed borderline resectable pancreatic cancer.Cancer Med. 2017 Jul;6(7):1552-1562. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1104. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 28639410 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical resection rates after neoadjuvant therapy for localized pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: meta-analysis.Br J Surg. 2022 Dec 13;110(1):34-42. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znac354. Br J Surg. 2022. PMID: 36346716
-
Contemporary management of borderline resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2019 May;23(2):97-108. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.2.97. Epub 2019 May 31. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2019. PMID: 31225409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Tumor Microenvironment of Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 21;12(10):3076. doi: 10.3390/cancers12103076. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33096881 Free PMC article.
-
Concepts and Outcomes of Perioperative Therapy in Stage IA-III Pancreatic Cancer-A Cross-Validation of the National Cancer Database (NCDB) and the German Cancer Registry Group of the Society of German Tumor Centers (GCRG/ADT).Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 9;14(4):868. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040868. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205616 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

