Insights on SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Interactions With the Renin-Angiotensin System
- PMID: 33042994
- PMCID: PMC7525006
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.559841
Insights on SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Interactions With the Renin-Angiotensin System
Abstract
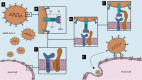
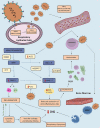
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2/human/Wuhan/X1/2019, a virus belonging to the species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus, and the recognition of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a pandemic have highly increased the scientific research regarding the pathogenesis of COVID-19. The Renin Angiotensin System (RAS) seems to be involved in COVID-19 natural course, since studies suggest the membrane-bound Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) works as SARS-CoV-2 cellular receptor. Besides the efforts of the scientific community to understand the virus' molecular interactions with human cells, few studies summarize what has been so far discovered about SARS-CoV-2 signaling mechanisms and its interactions with RAS molecules. This review aims to discuss possible SARS-CoV-2 intracellular signaling pathways, cell entry mechanism and the possible consequences of the interaction with RAS components, including Angiotensin II (Ang II), Angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)], Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), ACE2, Angiotensin II receptor type-1 (AT1), and Mas Receptor. We also discuss ongoing clinical trials and treatment based on RAS cascade intervention. Data were obtained independently by the two authors who carried out a search in the PubMed, Embase, LILACS, Cochrane, Scopus, SciELO and the National Institute of Health databases using Medical Subject Heading terms as "SARS-CoV-2," "COVID-19," "Renin Angiotensin System," "ACE2," "Angiotensin II," "Angiotensin-(1-7)," and "AT1 receptor." Similarly to other members of Coronaviridae family, the molecular interactions between the pathogen and the membrane-bound ACE2 are based on the cleavage of the spike glycoprotein (S) in two subunits. Following the binding of the S1 receptor-binding domain (RBD) to ACE2, transmembrane protease/serine subfamily 2 (TMPRSS2) cleaves the S2 domain to facilitate membrane fusion. It is very likely that SARS-CoV-2 cell entry results in downregulation of membrane-bound ACE2, an enzyme that converts Ang II into Ang-(1-7). This mechanism can result in lung injury and vasoconstriction. In addition, Ang II activates pro-inflammatory cascades when binding to the AT1 Receptor. On the other hand, Ang-(1-7) promotes anti-inflammatory effects through its interactions with the Mas Receptor. These molecules might be possible therapeutic targets for treating COVID-19. Thus, the understanding of SARS-CoV-2 intracellular pathways and interactions with the RAS may clarify COVID-19 physiopathology and open perspectives for new treatments and strategies.
Keywords: ACE2; AT1 receptor; Ang II; Ang-(1-7); COVID-19; Renin Angiotensin System; SARS-CoV-2; pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2020 Costa, Perez, Palmeira, Macedo e Cordeiro, Ribeiro, Lanza and Simões e Silva.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

