The Role of Lipids in the Initiation of α-Synuclein Misfolding
- PMID: 33042996
- PMCID: PMC7523214
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.562241
The Role of Lipids in the Initiation of α-Synuclein Misfolding
Abstract
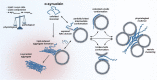
The aggregation of α-synuclein (α-syn) is inseparably connected to Parkinson's disease (PD). It is now well-established that certain forms of α-syn aggregates, oligomers and fibrils, can exert neurotoxicity in synucleinopathies. With the exception of rare familial forms, the vast majority of PD cases are idiopathic. Understanding the earliest molecular mechanisms that cause initial α-syn misfolding could help to explain why PD affects only some individuals and others not. Factors that chaperone the transition of α-syn's physiological to pathological function are of particular interest, since they offer opportunities for intervention. The relationship between α-syn and lipids represents one of those factors. Membrane interaction is crucial for normal cellular function, but lipids also induce the aggregation of α-syn, causing cell toxicity. Also, disease-causing or risk-factor mutations in genes related to lipid metabolism like PLA2G6, SCARB2 or GBA1 highlight the close connection between PD and lipids. Despite the clear link, the ambivalent interaction has not been studied sufficiently so far. In this review, we address how α-syn interacts with lipids and how they can act as key factor for orchestrating toxic conversion of α-syn. Furthermore, we will discuss a scenario in which initial α-syn aggregation is determined by shifts in lipid/α-syn ratio as well as by dyshomeostasis of membrane bound/unbound state of α-syn.
Keywords: Parkisnon’s disease; alpha synuclein (α-syn); alpha synuclein accumulation; alpha synuclein oligomers; lipid turnover.
Copyright © 2020 Kiechle, Grozdanov and Danzer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alteration of Structure and Aggregation of α-Synuclein by Familial Parkinson's Disease Associated Mutations.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(7):656-676. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160314151706. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 26972727 Review.
-
α-Synuclein misfolding and aggregation: Implications in Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019 Oct;1867(10):890-908. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019. PMID: 30853581 Review.
-
Lipids: Key Players That Modulate α-Synuclein Toxicity and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 7;21(9):3301. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093301. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32392751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Alpha-Synuclein With Lipids: Mitochondrial Cardiolipin as a Critical Player in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2020 Oct 6;14:578993. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.578993. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33122994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha synuclein and inflammaging.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 15;11(2):e41981. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41981. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39897785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate interacts with alpha-synuclein and initiates its aggregation and formation of Parkinson's disease-related fibril polymorphism.Acta Neuropathol. 2023 May;145(5):573-595. doi: 10.1007/s00401-023-02555-3. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Acta Neuropathol. 2023. PMID: 36939875 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophospholipids: A Potential Drug Candidates for Neurodegenerative Disorders.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 3;10(12):3126. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123126. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α-Synuclein: An All-Inclusive Trip Around its Structure, Influencing Factors and Applied Techniques.Front Chem. 2021 Jul 7;9:666585. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.666585. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34307295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Untwisted α-Synuclein Filaments Formed in the Presence of Lipid Vesicles.Biochemistry. 2022 Sep 6;61(17):1766-1773. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00283. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Biochemistry. 2022. PMID: 36001818 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Coaggregation in Caribbean Atypical Parkinsonism: The Contribution of Annonacin.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;51(4):e70026. doi: 10.1111/nan.70026. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40702589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd-Elhadi S., Honig A., Simhi-Haham D., Schechter M., Linetsky E., Ben-Hur T., et al. (2015). Total and proteinase K-resistant alpha-synuclein levels in erythrocytes, determined by their ability to bind phospholipids, associate with Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 5:11120. 10.1038/srep11120 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

