Multiple rapid swallows and rapid drink challenge in patients with esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction on high-resolution manometry
- PMID: 33043557
- PMCID: PMC7902305
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.14000
Multiple rapid swallows and rapid drink challenge in patients with esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction on high-resolution manometry
Abstract
Background: Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO) as defined by Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders (CCv3.0) encompasses a broad range of diagnoses, thus posing clinical challenges. Our aims were to evaluate multiple rapid swallow (MRS) and rapid drink challenge (RDC) during high-resolution manometry (HRM) to aid identifying clinically relevant EGJOO.
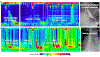
Methods: Patients with a HRM diagnosis of EGJOO based on CCv3.0 that also completed MRS and RDC during HRM and barium esophagram were retrospectively identified. Radiographic EGJOO (RAD-EGJOO) was defined by either liquid barium retention or delayed passage of a barium tablet on barium esophagram. Thirty healthy asymptomatic controls that completed HRM were also included. MRS involved drinking 2 mL for 5 successive swallows. RDC involved rapid drinking of 200 mL liquid. Integrated relaxation pressure (IRP) and presence of panesophageal pressurization (PEP) during MRS and RDC were assessed.
Key results: One hundred one patients, mean (SD) age 56 (16) years, were included; 32% had RAD-EGJOO, 68% did not. RAD-EGJOO patients more frequently had elevated (>12 mmHg) upright IRP (100%), MRS-IRP (56%), RDC-IRP (53%), and PEP during RDC (66%) than both controls [17%; 0%; 7%; 3%] and patients without RAD-EGJOO [83%; 35%; 39%; 41%] Having IRP >12 mmHg during both MRS and RDC was twice as likely to be associated with RAD-EGJOO (19%) than those without RAD-EGJOO (9%) among patients with upright IRP >12 mmHg.
Conclusions and inferences: Adjunctive HRM maneuvers MRS and RDC appear to help identify clinically significant EGJOO. While future outcome studies are needed, comprehensive multimodal evaluation helps clarify relevance of EGJOO on HRM.
Keywords: achalasia; diagnostic tests; dysphagia; endoscopy; motility.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement: Clinical use of esophageal manometry. Gastroenterology. 2005;128(1):207–208. - PubMed
-
- Pandolfino JE, Ghosh SK, Rice J, Clarke JO, Kwiatek MA, Kahrilas PJ. Classifying esophageal motility by pressure topography characteristics: a study of 400 patients and 75 controls. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103(1):27–37. - PubMed
-
- Clayton SB, Patel R, Richter JE. Functional and Anatomic Esophagogastic Junction Outflow Obstruction: Manometry, Timed Barium Esophagram Findings, and Treatment Outcomes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(6):907–911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

