Leptomeningitis in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 33044165
- PMCID: PMC7861636
- DOI: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2020.20063
Leptomeningitis in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
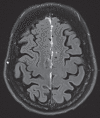
In this case report, we describe the case of a patient given the presumptive diagnosis of rheumatoid leptomeningitis on the basis of clinical findings and clinical response to antirheumatic medications after other causes of meningitis were excluded. Numerous case reports describe rheumatoid meningitis; however, rheumatoid leptomeningitis, in the absence of pachymeningitis, is a rare phenomenon. As such, the literature about it is scant. This unique case provides an opportunity to further characterize the symptoms and radiological findings of leptomeningitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Piecyk M, Schur P. Neurologic manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis [Internet] UpToDate. 2019. Aug 15, Available from: https://www-uptodate-com.ezproxy-so.library.usyd.edu.au/contents/neurolo....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials