Rubella virus-associated chronic inflammation in primary immunodeficiency diseases
- PMID: 33044342
- PMCID: PMC7730704
- DOI: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000694
Rubella virus-associated chronic inflammation in primary immunodeficiency diseases
Abstract
Purpose of the review: The aim of this article is to summarize recent data on rubella virus (RuV) vaccine in chronic inflammation focusing on granulomas in individuals with primary immunodeficiencies (PIDs).
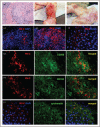
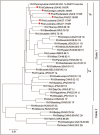
Recent findings: The live attenuated RuV vaccine has been recently associated with cutaneous and visceral granulomas in children with various PIDs. RuV vaccine strain can persist for decades subclinically in currently unknown body site(s) before emerging in granulomas. Histologically, RuV is predominately localized in M2 macrophages in the granuloma centers. Multiple mutations accumulate during persistence resulting in emergence of immunodeficiency-related vaccine-derived rubella viruses (iVDRVs) with altered immunological, replication, and persistence properties. Viral RNA was detected in granuloma biopsies and nasopharyngeal secretions and infectious virus were isolated from the granuloma lesions. The risk of iVDRV transmissibility to contacts needs to be evaluated. Several broad-spectrum antiviral drugs have been tested recently but did not provide significant clinical improvement. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation remains the only reliable option for curing chronic RuV-associated granulomas in PIDs.
Summary: Persistence of vaccine-derived RuVs appears to be a crucial factor in a significant proportion of granulomatous disease in PIDs. RuV testing of granulomas in PID individuals might help with case management.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Bousfiha AA, Jeddane L, Ailal F, et al. Primary immunodeficiency diseases worldwide: more common than generally thought. J Clin Immunol 2013; 33:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Chiam LY, Verhagen MM, Haraldsson A, et al. Cutaneous granulomas in ataxia telangiectasia and other primary immunodeficiencies: reflection of inappropriate immune regulation? Dermatology 2011; 223:13–19. - PubMed
-
- Nanda A, Al-Herz W, Al-Sabah H, Al-Ajmi H. Noninfectious cutaneous granulomas in primary immunodeficiency disorders: report from a national registry. Am J Dermatopathol 2014; 36:832–837. - PubMed
-
- Pagan AJ, Ramakrishnan L. The formation and function of granulomas. Annu Rev Immunol 2018; 36:639–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

