The Effect of Venlafaxine on Electrocardiogram Intervals During Treatment for Depression in Older Adults
- PMID: 33044352
- PMCID: PMC7606781
- DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000001287
The Effect of Venlafaxine on Electrocardiogram Intervals During Treatment for Depression in Older Adults
Abstract
Purpose/background: Venlafaxine is a commonly used antidepressant with both serotonergic and noradrenergic activity. There are concerns that it may prolong the corrected QT interval (QTc), and older adults may be at higher risk for this adverse effect, especially at higher dosages of the medication.
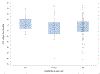
Methods/procedures: In this secondary analysis of a prospective clinical trial, we measured changes in QTc and other electrocardiogram (ECG) parameters in 169 adults 60 years or older with a major depressive disorder treated acutely with venlafaxine extended release up to 300 mg daily. We examined the relationship of venlafaxine dosage and ECG parameters, as well as the relationship between serum levels of venlafaxine and ECG parameters.
Findings/results: Venlafaxine exposure was not associated with an increase in QTc. Heart rate increased with venlafaxine treatment, whereas the PR interval shortened, and QRS width did not change significantly. The QTc change from baseline was not associated with venlafaxine dosages or serum concentrations. Age, sex, cardiovascular comorbidities, and depression remission status did not predict changes in QTc with venlafaxine.
Implications/conclusions: Venlafaxine treatment did not prolong QTc or other ECG parameters, even in high dosages in older depressed adults. These findings indicate that venlafaxine does not significantly affect cardiac conduction in most older patients.
Figures

References
-
- Staab JP, Evans DL. Efficacy of venlafaxine in geriatric depression. Depression and anxiety. 2000;12:63–8. - PubMed
-
- Owen JR, Nemeroff CB. New antidepressants and the cytochrome P450 system: focus on venlafaxine, nefazodone, and mirtazapine. Depress Anxiety. 1998;7 Suppl 1:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Marshe VS, Maciukiewicz M, Rej S, et al. Norepinephrine Transporter Gene Variants and Remission From Depression With Venlafaxine Treatment in Older Adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174:468–75. - PubMed
-
- Debonnel G, Saint-Andre E, Hebert C, et al. Differential physiological effects of a low dose and high doses of venlafaxine in major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007;10:51–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

