Childhood HIV-associated nephropathy: 36 years later
- PMID: 33044676
- PMCID: PMC8061423
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-020-04756-4
Childhood HIV-associated nephropathy: 36 years later
Abstract
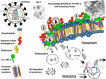
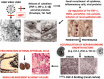
HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN) predominantly affects people of African ancestry living with HIV who do not receive appropriate antiretroviral therapy (ART). Childhood HIVAN is characterized by heavy proteinuria and decreased kidney function. Kidney histology shows mesangial expansion, classic or collapsing glomerulosclerosis, and microcystic renal tubular dilatation leading to kidney enlargement. The pathogenesis of HIVAN involves the kidney recruitment of inflammatory cells and the infection of kidney epithelial cells. In addition, both viral and genetic factors play key roles in this disease. Modern ART has improved the outcome and decreased the prevalence of childhood HIVAN. However, physicians have had modest success providing chronic ART to children and adolescents, and we continue to see children with HIVAN all over the world. This article discusses the progress made during the last decade in our understanding of the pathogenesis and treatment of childhood HIVAN, placing particular emphasis on the mechanisms that mediate the infection of kidney epithelial cells, and the roles of cytokines, the HIV-Tat gene, and the Apolipoprotein-1 (APOL1) gene risk variants in this disease. In view of the large number of children living with HIV at risk of developing HIVAN, better prevention and treatment programs are needed to eradicate this disease.
Keywords: APOL-1; Antiretroviral therapy; HIV nephropathy; HIV-Tat; Heparan sulfate proteoglycans; Infection of podocytes; Kidney epithelial cells; Pediatric AIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Rao TK, Filippone EJ, Nicastri AD, Landesman SH, Frank E, Chen CK, Friedman EA. Associated focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:669–673. - PubMed
-
- Strauss J, Abitbol C, Zilleruelo G, Scott G, Paredes A, Malaga S, Montane B, Mitchell C, Parks W, Pardo V. Renal disease in children with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:625–630. - PubMed
-
- Ray PE, Rakusan T, Loechelt BJ, Selby DM, Liu XH, Chandra RS. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated nephropathy in children from the Washington, D.C. area: 12 years’ experience. Semin Nephrol. 1998;18:396–405. - PubMed
-
- Children, HIV and AIDS. Global Snapshot 2019. https://data.unicef.org/resources/children-hiv-aids-global-snapshot/data.unicef.org
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

