Greater male than female variability in regional brain structure across the lifespan
- PMID: 33044802
- PMCID: PMC8675415
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25204
Greater male than female variability in regional brain structure across the lifespan
Abstract
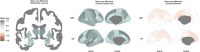
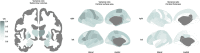
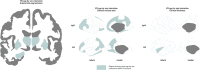
For many traits, males show greater variability than females, with possible implications for understanding sex differences in health and disease. Here, the ENIGMA (Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis) Consortium presents the largest-ever mega-analysis of sex differences in variability of brain structure, based on international data spanning nine decades of life. Subcortical volumes, cortical surface area and cortical thickness were assessed in MRI data of 16,683 healthy individuals 1-90 years old (47% females). We observed significant patterns of greater male than female between-subject variance for all subcortical volumetric measures, all cortical surface area measures, and 60% of cortical thickness measures. This pattern was stable across the lifespan for 50% of the subcortical structures, 70% of the regional area measures, and nearly all regions for thickness. Our findings that these sex differences are present in childhood implicate early life genetic or gene-environment interaction mechanisms. The findings highlight the importance of individual differences within the sexes, that may underpin sex-specific vulnerability to disorders.
© 2020 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: OAA: Speaker's honorarium from Lundbeck, Consultant of HealthLyti; PA: Received payments for consultancy to Shire/Takeda, Medic, educational/research awards from Shire/Takeda, GW Pharma, Janssen‐Cila, speaker at sponsored events for Shire, Flynn Pharma, Medic; TB: advisory or consultancy role for Lundbeck, Medice, Neurim Pharmaceuticals, Oberberg GmbH, Shire, and Infectopharm, conference support or speaker's fee by Lilly, Medice, and Shire, received royalities from Hogrefe, Kohlhammer, CIP Medien, Oxford University Press ‐ the present work is unrelated to the above grants and relationship; DB: serves as an unpaid scientific consultant for an EU‐funded neurofeedback trial that is unrelated to the present work; HB: Advisory Board, Nutricia Australi; CRKC: received partial research support from Biogen, Inc. (Boston, USA) for work unrelated to the topic of this manuscript; BF: received educational speaking fees from Medice; HJG: received travel grants and speakers honoraria from Fresenius Medical Care, Neuraxpharm, Servier and Janssen Cilag as well as research funding from Fresenius Medical Care; NJ and PMT: MPI of a research related grant from Biogen, Inc., for research unrelated to the contents of this manuscript; JK: given talks at educational events sponsored by Medic; all funds are received by King's College London and used for studies of ADHD; DM‐C: receives fees from UpToDate, Inc and Elsevier, all unrelated to the current work; AMM: received research support from Eli Lilly, Janssen, and the Sackler Foundation, and speaker fees from Illumina and Janssen; DJS: received research grants and/or honoraria from Lundbeck and Sun. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Arden, R. , & Plomin, R. (2006). Sex differences in variance of intelligence across childhood. Personality and Individual Differences, 41, 39–48.
-
- Aron, A. R. , Robbins, T. W. , & Poldrack, R. A. (2004). Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(4), 170–177. - PubMed
-
- Baaré, W. , Pol, H. , Boomsma, D. I. , & Posthuma, D. (2001). Quantitative genetic modeling of variation in human brain morphology. Cerebral Cortex, 111(9), 816–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- T32 MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NF-SI-0616-10040/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- U01 NS105509/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000840/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085604/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH071616/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059259/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 MH068540/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103472/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH096957/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0300189/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R37 MH101495/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH097435/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH118695/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062873/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019771/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- ERC-230374/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- K24 MH094614/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG064001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03AG064001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 104036/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 5T32MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- G03001896 to J Kuntsi/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH056584/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH120482/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH117014/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- ERC-2010-StG-263234/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- R01 EB005846/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NIHR/MRC (14/23/17)/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- FRN114887/CIHR/Canada
- U01 AG068057/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54EB020403/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH104284/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB006841/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116147/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 287378/CIHR/Canada
- R01 MH129742/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113619/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P20GM130447/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH120080/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S035818/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 AG058507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH117601/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD050735/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32AG058507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH099232/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH106324/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB020062/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM130447/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG058854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG058/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057892/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH101367/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 064846/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- FRN126053/CIHR/Canada
- U24 RR021992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH085096/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101495/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH084803/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17209/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH119219/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 216767/Z/19/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH083246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH085953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH119243/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 MH089257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB020407/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101486/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH115206/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG059874/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0500092/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom

