SID-2 negatively regulates development likely independent of nutritional dsRNA uptake
- PMID: 33044912
- PMCID: PMC8081039
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1827619
SID-2 negatively regulates development likely independent of nutritional dsRNA uptake
Abstract
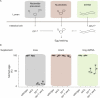
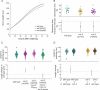
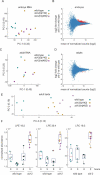
RNA interference (RNAi) is a gene regulatory mechanism based on RNA-RNA interaction conserved through eukaryotes. Surprisingly, many animals can take-up human-made double stranded RNA (dsRNA) from the environment to initiate RNAi suggesting a mechanism for dsRNA-based information exchange between organisms and their environment. However, no naturally occurring example has been identified since the discovery of the phenomenon 22 years ago. Therefore it remains enigmatic why animals are able to take up dsRNA. Here, we explore other possible functions by performing phenotypic studies of dsRNA uptake deficient sid-2 mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans. We find that SID-2 does not have a nutritional role in feeding experiments using genetic sensitized mutants. Furthermore, we use robot assisted imaging to show that sid-2 mutants accelerate growth rate and, by maternal contribution, body length at hatching. Finally, we perform transcriptome and lipidome analysis showing that sid-2 has no effect on energy storage lipids, but affects signalling lipids and the embryo transcriptome. Overall, these results suggest that sid-2 has mild effects on development and is unlikely functioning in the nutritional uptake of dsRNA. These findings broaden our understanding of the biological role of SID-2 and motivate studies identifying the role of environmental dsRNA uptake.
Keywords: Environmental RNAi; RNA communication; RNAi; double stranded RNA; nutrition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SID-1 is a dsRNA-selective dsRNA-gated channel.RNA. 2011 Jun;17(6):1057-65. doi: 10.1261/rna.2596511. Epub 2011 Apr 7. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21474576 Free PMC article.
-
SID-1 Functions in Multiple Roles To Support Parental RNAi in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2017 Oct;207(2):547-557. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300067. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28751423 Free PMC article.
-
SID-1 Domains Important for dsRNA Import in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Dec 4;7(12):3887-3899. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300308. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 29025917 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic RNAi in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:95-100. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.060. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381285 Review.
-
Structural Perspective of the Double-Stranded RNA Transport Mechanism by SID-1 Family Proteins.Biol Pharm Bull. 2024;47(10):1610-1615. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b24-00419. Biol Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 39358240 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant and animal small RNA communications between cells and organisms.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Mar;23(3):185-203. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00425-y. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34707241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Canalisation and plasticity on the developmental manifold of Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Syst Biol. 2023 Nov 9;19(11):e11835. doi: 10.15252/msb.202311835. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Mol Syst Biol. 2023. PMID: 37850520 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient siRNA delivery to murine melanoma cells via a novel genipin-based nano-polymer.Nanoscale Adv. 2024 Jul 19;6(18):4704-4723. doi: 10.1039/d4na00363b. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 39263399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siomi H, Siomi MC. On the road to reading the RNA-interference code. Nature. 2009;457(7228):396–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources