Overweight and obesity among Vietnamese school-aged children: National prevalence estimates based on the World Health Organization and International Obesity Task Force definition
- PMID: 33044981
- PMCID: PMC7549813
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240459
Overweight and obesity among Vietnamese school-aged children: National prevalence estimates based on the World Health Organization and International Obesity Task Force definition
Abstract
Background: Overweight and obesity is a severe global health issue in both developed and developing nations. This study aims to estimate the national prevalence of overweight and obesity among school-aged children in Vietnam.
Method: We conducted a national cross-sectional study on 2788 children aged from 11-14 years old from September to November 2018. We applied the WHO 2007 and IOTF criteria to estimate the prevalence of overweight and obesity among participants. Poison regression analysis with cluster sampling adjustment was employed to assess associated factors with obesity and overweight. Metadata on sociodemographic characteristics, physical measurements, and lifestyle behaviors were also extracted to investigate these factors in association with overweight and obesity prevalence.
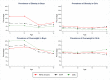
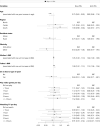
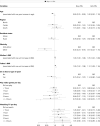
Results: The prevalences of overweight and obesity in Vietnamese children were 17.4% and 8.6%, respectively by WHO Z-score criteria, and 17.1% and 5.4%, according to the IOTF reference. Using WHO Z-score yielded a higher prevalence of obesity than the IOTF and CDC criteria of all ages and both sexes. The proportions of overweight and obesity were substantially higher among boys than girls across ages. Parental BMI was shown to be a significant factor associated with overweight/obesity status in both girls and boys. Only for boys, age (PR = 0.83, 95% CI 0.76-0.90) and belonging to ethnic minorities (PR = 0.43, 95% CI 0.24-0.76) were significant risk factors for overweight/obesity.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate a high prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Vietnam, especially in boys.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of overweight/obesity in relation to dietary habits and lifestyle among 7-17 years old children and adolescents in Lithuania.BMC Public Health. 2015 Oct 1;15:1001. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-2340-y. BMC Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26429124 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Underweight, Overweight and Obesity in School-Aged Children in the Urban Area of the Northwestern Part of Romania.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 13;18(10):5176. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105176. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34068152 Free PMC article.
-
Overweight and obesity of school-age children in El Salvador according to two international systems: a population-based multilevel and spatial analysis.BMC Public Health. 2020 May 14;20(1):687. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08747-w. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32410611 Free PMC article.
-
Gender differences and climate zones in overweight and obesity prevalence in European elementary school children from 2000 to 2020: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2023 Sep 21;11:1198877. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1198877. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37808999 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of obesity among adolescents in Eastern Turkey: A cross-sectional study with a review of the local literature.Niger J Clin Pract. 2019 Aug;22(8):1070-1077. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_418_18. Niger J Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 31417049
Cited by
-
Doctors' Perception Regarding Bariatric Surgery and Major Barriers in Referral of Morbidly Obese Patients for Surgery in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.Cureus. 2023 Jun 12;15(6):e40305. doi: 10.7759/cureus.40305. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37448399 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Health Belief Model to Assess Predictors of Weight Management Behaviour Intention Among Civil Servants in Ethiopia: A Mixed Method Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Oct 26;16:3339-3352. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S431146. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37908630 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 6;12:706978. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.706978. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34552557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence, determinants, intervention strategies and current gaps in addressing childhood malnutrition in Vietnam: a systematic review.BMC Public Health. 2024 Apr 4;24(1):960. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18419-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38575928 Free PMC article.
-
Association between rs4994 variant in β3-Adrenergic receptor and obesity in Vietnamese preschool-age children, independent of eating behaviors.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Sep 18;24(1):594. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05073-7. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39294633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight 2018 [cited 2019 18 March]. Available from: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- World Health Organization. Global health risks: mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks. Geneva: World Health Organization., 2009.
-
- Mazidi M, Banach M, Kengne AP, Lipid, Blood Pressure Meta-analysis Collaboration G. Prevalence of childhood and adolescent overweight and obesity in Asian countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of medical science: AMS. 2018;14(6):1185–203. Epub 2018/11/06. 10.5114/aoms.2018.79001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

