SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 33045718
- PMCID: PMC8092461
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2852-1
SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies.Nature. 2024 Apr;628(8008):E2. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07344-w. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38565636 No abstract available.
Abstract
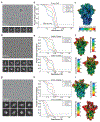
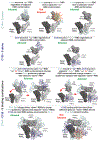
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic presents an urgent health crisis. Human neutralizing antibodies that target the host ACE2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein1-5 show promise therapeutically and are being evaluated clinically6-8. Here, to identify the structural correlates of SARS-CoV-2 neutralization, we solved eight new structures of distinct COVID-19 human neutralizing antibodies5 in complex with the SARS-CoV-2 spike trimer or RBD. Structural comparisons allowed us to classify the antibodies into categories: (1) neutralizing antibodies encoded by the VH3-53 gene segment with short CDRH3 loops that block ACE2 and bind only to 'up' RBDs; (2) ACE2-blocking neutralizing antibodies that bind both up and 'down' RBDs and can contact adjacent RBDs; (3) neutralizing antibodies that bind outside the ACE2 site and recognize both up and down RBDs; and (4) previously described antibodies that do not block ACE2 and bind only to up RBDs9. Class 2 contained four neutralizing antibodies with epitopes that bridged RBDs, including a VH3-53 antibody that used a long CDRH3 with a hydrophobic tip to bridge between adjacent down RBDs, thereby locking the spike into a closed conformation. Epitope and paratope mapping revealed few interactions with host-derived N-glycans and minor contributions of antibody somatic hypermutations to epitope contacts. Affinity measurements and mapping of naturally occurring and in vitro-selected spike mutants in 3D provided insight into the potential for SARS-CoV-2 to escape from antibodies elicited during infection or delivered therapeutically. These classifications and structural analyses provide rules for assigning current and future human RBD-targeting antibodies into classes, evaluating avidity effects and suggesting combinations for clinical use, and provide insight into immune responses against SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The Rockefeller University has filed a provisional patent application in connection with this work on which D.F.R. and M.C.N. are inventors (US 63/021,387).
Figures









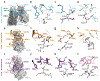

Update of
-
Structural classification of neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain suggests vaccine and therapeutic strategies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 30:2020.08.30.273920. doi: 10.1101/2020.08.30.273920. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nature. 2020 Dec;588(7839):682-687. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2852-1. PMID: 32869026 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Additional References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

