Cardiopulmonary resuscitation in prone position: A scoping review
- PMID: 33046293
- PMCID: PMC7481259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.08.097
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation in prone position: A scoping review
Abstract
Introduction: The ongoing pandemic of COVID-19 brought to the fore prone positioning as treatment for patients with acute respiratory failure. With the increasing number of patients in prone position, both spontaneously breathing and mechanically ventilated, cardiac arrest in this position is more likely to occur. This scoping review aimed to summarize the available evidence on cardiopulmonary resuscitation in prone position ('reverse CPR') and knowledge or research gaps to be further evaluated. The protocol of this scoping review was prospectively registered on 10th May 2020 in Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/nfuh9).
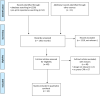
Methods: We searched PubMed, EMBASE, MEDLINE and pre-print repositories (bioRxiv and medRxiv) for simulation, pre-clinical and clinical studies on reverse CPR until 31st May 2020.
Results: We included 1 study on manikins, 31 case reports (29 during surgery requiring prone position) and 2 nonrandomized studies describing reverse CPR. No studies were found regarding reverse CPR in patients with COVID-19.
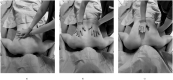
Conclusions: Even if the algorithms provided by the guidelines on basic and advanced life support remain valid in cardiac arrest in prone position, differences exist in the methods of performing CPR. There is no clear evidence of superiority in terms of effectiveness of reverse compared to supine CPR in patients with cardiac arrest occurring in prone position. The quality of evidence is low and knowledge gaps (e.g. protocols, training of healthcare personnel, devices for skill acquisition) should be fulfilled by further research. Meanwhile, a case-by-case evaluation of patient and setting characteristics should guide the decision on how to start CPR in such cases.
Keywords: COVID-19; Prone CPR; Prone position; Reverse CPR.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures

References
-
- Link M.S., Berkow L.C., Kudenchuk P.J., Halperin H.R., Hess E.P., Moitra V.K., et al. Part 7: adult advanced cardiovascular life support: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines update for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2015;132:S444–S464. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000261. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Piehl M., Brown R. Use of extreme position changes in acute respiratory failure. Crit Care Med. 1976;4:13–14. - PubMed
-
- Coppo A., Bellani G., Winterton D., Di Pierro M., Soria A., Faverio P., et al. Feasibility and physiological effects of prone positioning in non-intubated patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 (PRON-COVID): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30268-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

