Leveraging Heterogeneity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus for New Therapies
- PMID: 33046407
- PMCID: PMC8667782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2020.09.009
Leveraging Heterogeneity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus for New Therapies
Abstract
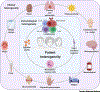
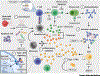
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem, chronic autoimmune disease where treatment varies by patient and disease activity. Strong preclinical results and clinical correlates have motivated development of many drugs, but many of these have failed to achieve efficacy in clinical trials. FDA approval of belimumab in 2011 was the first successful SLE drug in nearly six decades. In this article, we review insights into the molecular and clinical heterogeneity of SLE from transcriptomics studies and detail their potential impact on drug development and clinical practices. We critically examine the pipeline of SLE drugs, including past failures and their associated lessons and current promising approaches. Finally, we identify opportunities for integrating these findings and drug development with new multidisciplinary advances to enhance future SLE treatment.
Keywords: patient heterogeneity; personalized medicine; systemic lupus erythematosus; systems immunology; therapies; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Al Sawah S, et al., SAT0423 Understanding Delay in Diagnosis, Access to Care and Satisfaction with Care in Lupus: Findings from a Cross-Sectional Online Survey in the United States. Ann. Rheum. Dis, 2015. 74(Suppl 2): p. 812–812.
-
- Murphy G. and Isenberg D, Effect of gender on clinical presentation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2013. 52(12): p. 2108–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

