Detection of Giardia lamblia by Microscopic Examination, Rapid Chromatographic Immunoassay Test, and Molecular Technique
- PMID: 33047079
- PMCID: PMC7541033
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10287
Detection of Giardia lamblia by Microscopic Examination, Rapid Chromatographic Immunoassay Test, and Molecular Technique
Abstract
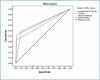
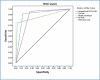
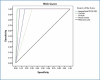
Background Giardia lamblia is a pathogenic intestinal flagellate transmitted by the ingestion of contaminated water or food with the cyst stage of the parasite. Giardiasis can cause severe acute diarrhea and malabsorption or may persist as a chronic infection. Effective treatment and control measures depend on proper laboratory diagnosis using diagnostic methods with high sensitivity and specificity. Objective To compare the sensitivity and specificity of direct smear, Ritchie sedimentation technique, two brands of rapid chromatographic immunoassay test, and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for the detection of G. lamblia in clinical human fecal samples. Materials and methods Unpreserved 100 stool specimens were collected in clean plastic containers and labeled with the patient's information and examined through light microscopy, immunochromatographic test (ICTs), and real-time PCR. Results Out of 100 fresh stool samples obtained from workers analyzed, real-time PCR targeting the SSU rRNA gene was able to detect Giardia deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in (42) samples followed by ImmunoCard STAT! (31) samples (Meridian Bioscience, Germany), direct smear (23) samples, CerTest (19) samples (Biotec, Zaragoza, Spain), and Ritchie technique (17) samples. Real-time PCR was the most sensitive for the diagnosis of G. lamblia in comparison to the other techniques. Conclusions All the techniques investigated were sensitive for the detection of G. lamblia in stool samples. Further studies are recommended using multiplex real-time PCR assay in order to increase the possibility of the presence or absence of the infection.
Keywords: diagnosis; giardia lamblia; icts; neglected diseases; parasites; real-time pcr; saudi arabia.
Copyright © 2020, Alharbi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PCR detection of Giardia lamblia in stool: targeting intergenic spacer region of multicopy rRNA gene.Mol Cell Probes. 2000 Jun;14(3):181-9. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.2000.0302. Mol Cell Probes. 2000. PMID: 10860716
-
Multiplex PCR detection of Cryptosporidium sp, Giardia lamblia and Entamoeba histolytica directly from dried stool samples from Guinea-Bissauan children with diarrhoea.Infect Dis (Lond). 2017 Sep;49(9):655-663. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2017.1320728. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Infect Dis (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28446068
-
Comparison of microscopy, real-time PCR and a rapid immunoassay for the detection of Giardia lamblia in human stool specimens.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007 Dec;13(12):1186-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01836.x. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007. PMID: 17949440
-
Giardiasis: An Overview.Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2019;13(2):134-143. doi: 10.2174/1872213X13666190618124901. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2019. PMID: 31210116 Review.
-
Is real-time PCR-based diagnosis similar in performance to routine parasitological examination for the identification of Giardia intestinalis, Cryptosporidium parvum/Cryptosporidium hominis and Entamoeba histolytica from stool samples? Evaluation of a new commercial multiplex PCR assay and literature review.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016 Feb;22(2):190.e1-190.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.10.019. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016. PMID: 26548509 Review.
Cited by
-
A 'One Health' perspective of Africa-wide distribution and prevalence of Giardia species in humans, animals and waterbodies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Parasitology. 2023 Aug;150(9):769-780. doi: 10.1017/S0031182023000513. Epub 2023 May 29. Parasitology. 2023. PMID: 37246558 Free PMC article.
-
Coprological and molecular prevalence of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in cattle and irrigation water from Beni-Suef Governorate, Egypt.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 24;15(1):26983. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10552-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40707581 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of Diagnostic Approaches for Human Giardiasis: Unveiling Optimal Strategies.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;14(4):364. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14040364. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of intestinal parasites and comparison of detection techniques for soil-transmitted helminths among newly arrived expatriate labors in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.PeerJ. 2024 Jan 26;12:e16820. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16820. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38288465 Free PMC article.
-
Making the Most of Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Tests: An Efficient Protocol to Recover DNA.Methods Protoc. 2024 Jan 15;7(1):8. doi: 10.3390/mps7010008. Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38251201 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giardiasis: an update review on sensitivity and specificity of methods for laboratorial diagnosis. Soares R, Tasca T. J Microbiol Methods. 2016;129:98–102. - PubMed
-
- Giardia and Cryptosporidium join the 'neglected diseases initiative'. Savioli L, Smith H, Thompson A. Trends Parasitol. 2006;22:203–208. - PubMed
-
- Management of chronic Giardia infection. Escobedo AA, Hanevik K, Almirall P, Cimerman S, Alfonso M. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014;12:1143–1157. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
