Incidence of Lichen Planus and Subsequent Mortality in Finnish Women
- PMID: 33047145
- PMCID: PMC9274926
- DOI: 10.2340/00015555-3664
Incidence of Lichen Planus and Subsequent Mortality in Finnish Women
Abstract
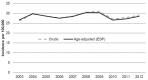
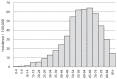
The incidence pattern of lichen planus (LP) and LP-related mortality are unknown. The aim of this study was to assess these factors, based on Finnish nationwide registry data including 13,378 women with LP diagnosed during 1969 to 2012. The incidence rate for LP in 2003 to 2012 was 28 per 100,000 woman-years age-adjusted to the European Standard Population. Mortality was assessed using the standardized mortality ratio (SMR) with national mortality rates as the reference. All-cause mortality was increased (SMR 1.07, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 1.02-1.11), with excess mortality from Hodgkin lymphoma (SMR 6.73, 95% CI 1.83-17.2), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (SMR 1.68, 95% CI 1.11-2.44), cancer of the oral cavity (SMR 10.5, 95% CI 5.99-17.0), cancer of the tongue (SMR 7.25, 95% CI 3.13-14.3), infections (SMR 1.78, 95% CI 1.14-2.64), respiratory diseases (SMR 1.31, 95% CI 1.07-1.57), and diseases of the digestive system (SMR 1.39, 95% CI 1.09-1.75). In conclusion, LP is a common disease and patients seem to have an impaired long-term prognosis.
Keywords: cause of death; epidemiology; incidence; mortality; lichen planus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence of lichen sclerosus and subsequent causes of death: a nationwide Finnish register study.BJOG. 2020 Jun;127(7):814-819. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.16175. Epub 2020 Mar 9. BJOG. 2020. PMID: 32065721
-
Cancer risk of Lichen planus: A cohort study of 13,100 women in Finland.Int J Cancer. 2018 Jan 1;142(1):18-22. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31025. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28857160
-
Mortality and causes of death for people with multiple sclerosis: a Finnish nationwide register study.J Neurol. 2025 May 2;272(5):370. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13112-1. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40314829 Free PMC article.
-
Lichen planus of the esophagus: what dermatologists need to know.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 Jul;65(1):175-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.029. Epub 2011 May 4. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21536343 Review.
-
[Lichen planus: fundamentals, clinical variants, histological features, and differential diagnosis].Hautarzt. 2020 Dec;71(12):1007-1021. doi: 10.1007/s00105-020-04717-w. Hautarzt. 2020. PMID: 33201324 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Esophageal lichen planus: Current knowledge, challenges and future perspectives.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 7;28(41):5893-5909. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i41.5893. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36405107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lichen Planus.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 1;8:737813. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.737813. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34790675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk of Vulvar HSIL and Penile Neoplasias in Anogenital Lichen Planus: A Case-Control Study.J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2025 Jul 1;29(3):288-292. doi: 10.1097/LGT.0000000000000879. Epub 2025 Feb 14. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2025. PMID: 39951645 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma proteins and inflammatory dermatoses: proteome-wide Mendelian randomization and colocalization analyses.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Jul 1;316(7):443. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03191-x. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38951247
-
Lichen Planus: What is New in Diagnosis and Treatment?Am J Clin Dermatol. 2024 Sep;25(5):735-764. doi: 10.1007/s40257-024-00878-9. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38982032 Review.
References
-
- Silverman S, Jr, Gorsky M, Lozada-Nur F. A prospective follow-up study of 570 patients with oral lichen planus: persistence, remission, and malignant association. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1985; 60: 30–34. - PubMed
-
- Carbone M, Arduino PG, Carrozzo M, Gandolfo S, Argiolas MR, Bertolusso G, et al. . Course of oral lichen planus: a retrospective study of 808 northern Italian patients. Oral Dis 2009; 15: 235–243. - PubMed
-
- Irvine C, Irvine F, Champion RH. Long-term follow-up of lichen planus. Acta Derm Venereol 1991; 71: 242–244. - PubMed
-
- Axell T, Rundquist L. Oral lichen planus – a demographic study. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1987; 15: 52–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical