Impact of a community-wide combination HIV prevention intervention on knowledge of HIV status among adolescents
- PMID: 33048875
- PMCID: PMC7810414
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002722
Impact of a community-wide combination HIV prevention intervention on knowledge of HIV status among adolescents
Abstract
Objective: To determine the impact of a community-wide combination HIV-prevention package (PopART Intervention) that includes universal testing and treatment (UTT) on knowledge of HIV status, among adolescents aged 15--19 years.
Design: The HPTN 071 (PopART) for Youth (P-ART-Y) study was nested within HPTN 071 (PopART), a three-arm, cluster-randomized trial conducted from 2013 through 2018 in 21 communities in Zambia and South Africa. Communities were randomly assigned to arm A (combination prevention intervention with universal ART), arm B (prevention intervention with ART provided according to local guidelines), or arm C (standard-of-care).
Methods: Knowledge of HIV status was measured using data collected during the third round of the PopART intervention in arms A and B (October 2016 to December 2017) and by conducting a cross-sectional survey (August to November 2017) in arm C communities to provide comparative data. The survey was conducted among ∼200 randomly selected adolescents in each community. We used linear regression of the 21 community-level values to make comparisons among trial arms.
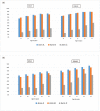
Results: Knowledge of HIV status was 78.2% (23 544/30 089) in arm A and 76.0% (24 417/32 148) in arm B communities, compared with 32.9% (698/2120) in arm C communities. Knowledge of HIV status varied by country, triplet, sex, and age. The adjusted mean difference was 42.3% between arm A with arm C, 95% CI 28.1-56.6, P less than 0.001 and 40.4% between arm B with arm C, 95% CI 24.6-56.2, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Implementation of a community-wide combination HIV-prevention package that includes UTT substantially enhanced knowledge of HIV status among adolescents.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- UNICEF UNAIDS. All In to end the Adolescent AIDS in Eastern and Southern Africa: Catalysing the HIV response for adolescents 2018 [updated 15th March]. Available from: https://reliefweb.int/report/world/all-eastern-and-southern-africa-catal....
-
- UNICEF. HIV prevention 2018 [cited 2019 12th March]. Available at: https://data.unicef.org/topic/hivaids/adolescents-young-people/.
-
- PHIA Project. A drop that counts. Available at: https://phia.icap.columbia.edu/.
-
- Makhema MJ, Wirth K, Pretorius Holme M, Gaolathe T, Mmalane M, Kadima E, et al. Impact of prevention and treatment interventions on population HIV incidence: rrimary results of the community-randomized Ya Tsie Botswana prevention project. 22nd International AIDS Conference Amsterdam, Netheralands. 2018.
-
- Iwuji CC, Orne-Gliemann J, Larmarange J, Balestre E, Thiebaut R, Tanser F, et al. ANRS 12249 TasP Study Group. Universal test and treat and the HIV epidemic in rural South Africa: a phase 4, open-label, community cluster randomised trial. Lancet HIV 2018; 5:e116–e125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

