The polymorphic inheritance of DIO2 rs225014 may predict body weight variation after Graves' disease treatment
- PMID: 33049131
- PMCID: PMC10528618
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000295
The polymorphic inheritance of DIO2 rs225014 may predict body weight variation after Graves' disease treatment
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to investigate the role of DIO2 polymorphisms rs225014 and rs12885300 in Graves' disease patients, mainly for controlling body weight following treatment.
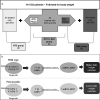
Methods: We genotyped 280 GD patients by the time of diagnosis and 297 healthy control individuals using a TaqMan SNP Genotyping technique. We followed up 141 patients for 18.94 ± 6.59 months after treatment.
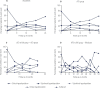
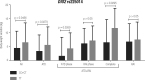
Results: There was no relationship between the investigated polymorphisms with susceptibility to GD and gain or loss of weight after GD treatment. However, the polymorphic inheritance (CC+CT genotype) of DIO2 rs225014 was associated with a lower body weight variation after GD treatment (4.26 ± 6.25 kg) when compared to wild type TT genotype (6.34 ± 7.26 kg; p = 0.0456 adjusted for the follow-up time). This data was confirmed by a multivariate analysis (p = 0.0138) along with a longer follow-up period (p = 0.0228), older age (p = 0.0306), treatment with radioiodine (p-value = 0.0080) and polymorphic inheritance of DIO2 rs12885300 (p = 0.0306).
Conclusion: We suggest that DIO2 rs225014 genotyping may have an auxiliary role in predicting the post-treatment weight behavior of GD patients.
Keywords: DIO2 gene; Graves’ Disease; polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Smith TJ, Hegedüs L. Graves’ Disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(16):1552-65. - PubMed
-
- Brent GA. Clinical practice. Graves’ disease. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2594-605. - PubMed
-
- Bartalena L. Diagnosis and management of Graves disease: a global overview. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013;9(12):724-34. - PubMed
-
- Bianco AC, Maia AL, da Silva WS, Christoffolete MA. Adaptive activation of thyroid hormone and energy expenditure. Biosci Rep. 2005;25(3-4):191-208. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
