The duration of infectiousness of individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33049331
- PMCID: PMC7547320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.10.009
The duration of infectiousness of individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Objectives: To summarise the evidence on the duration of infectiousness of individuals in whom SARS-CoV-2 ribonucleic acid is detected.
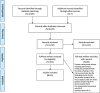
Methods: A rapid review was undertaken in PubMed, Europe PubMed Central and EMBASE from 1 January 2020 to 26 August 2020.
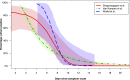
Results: We identified 15 relevant studies, including 13 virus culture and 2 contact tracing studies. For 5 virus culture studies, the last day on which SARS-CoV-2 was isolated occurred within 10 days of symptom onset. For another 5 studies, SARS-CoV-2 was isolated beyond day 10 for approximately 3% of included patients. The remaining 3 virus culture studies included patients with severe or critical disease; SARS-CoV-2 was isolated up to day 32 in one study. Two studies identified immunocompromised patients from whom SARS-CoV-2 was isolated for up to 20 days. Both contact tracing studies, when close contacts were first exposed greater than 5 days after symptom onset in the index case, found no evidence of laboratory-confirmed onward transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusion: COVID-19 patients with mild-to-moderate illness are highly unlikely to be infectious beyond 10 days of symptoms. However, evidence from a limited number of studies indicates that patients with severe-to-critical illness or who are immunocompromised, may shed infectious virus for longer.
Keywords: COVID-19; Contact tracing; Coronavirus; Infectiousness; Isolation; RNA; Review; SARS-CoV-2; Virus culture.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2 positive virus culture 7 weeks after onset of COVID-19 in an immunocompromised patient suffering from X chromosome-linked agammaglobulinemia.J Infect. 2021 Mar;82(3):414-451. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.10.025. Epub 2020 Oct 27. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 33121954 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Duration of culturable SARS-CoV-2 within different specimens among mild and severe COVID-19 patients: A longitudinal study.J Infect. 2021 Jul;83(1):e29-e31. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.04.025. Epub 2021 Apr 28. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 33932450 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Longitudinal study of a SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient with X-linked agammaglobulinemia.J Infect. 2021 Nov;83(5):607-635. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.07.028. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 34329678 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Infection-enhancing anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies recognize both the original Wuhan/D614G strain and Delta variants. A potential risk for mass vaccination?J Infect. 2021 Nov;83(5):607-635. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.08.010. Epub 2021 Aug 9. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 34384810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- John Hopkins University & Medicine. COVID-19 Dashboard 2020 [updated 5 Sep 2020; cited 2020 5 Sep]. Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

