Incidence of COVID-19 among returning travelers in quarantine facilities: A longitudinal study and lessons learned
- PMID: 33049360
- PMCID: PMC7547317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101901
Incidence of COVID-19 among returning travelers in quarantine facilities: A longitudinal study and lessons learned
Abstract
Introduction: The emergence of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) had resulted in an unpresented global pandemic. In the initial events, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia implemented mandatory quarantine of returning travelers in order to contain COVID-19 cases.
Materials and methods: This is a longitudinal study of the arriving travelers to Quarantine facilities and the prevalence of positive SARS-CoV-2 as detected by RT-PCR.
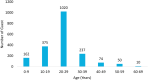
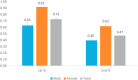
Results: During the study period, there was a total of 1928 returning travelers with 1273 (66%) males. The age range was 28 days-69 years. Of all the travelers, 23 (1.2%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. Of the first swab, 14/1928 (0.7%) tested positive. The positivity rate was 0.63% and 0.92% among males and females, respectively (P = 0.57). The second swab was positive in 9 (0.5%) of the other 1914 who were initially negative with a positivity rate of 0.39% and 0.62% among males and females, respectively (P = 0.49). There was no statistical difference in the positivity rates between first and second swab (P = 0.4). Of all travelers, 40 (n = 26, 1.3%) were admitted from the quarantine facility to the hospital due to COVID-19 related positive results or development of symptoms such as fever, cough, and respiratory symptoms; and 14 (0.7%) were admitted due to non-COVID-19 related illness.
Conclusion: This study showed the efforts put for facility quarantine and that such activity yielded a lower incidence of positive cases. There was a need to have a backup healthcare facility to accommodate those developing a medical need for evaluation and admission for non-COVID-19 related illnesses.
Keywords: COVID-19; Quarantine; SARS-CoV-2; Travelers.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

