Non-coding RNA biomarkers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33049362
- PMCID: PMC8035348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.10.001
Non-coding RNA biomarkers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Non-coding RNA biomarkers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma" [Semin. Cancer Biol. 75 (2021) 153-168].Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Feb;79:231-233. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.01.002. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 35074270 No abstract available.
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most lethal malignancies, which is usually diagnosed at an advanced stage. The late disease diagnosis, the limited availability of effective therapeutic interventions and lack of robust diagnostic biomarkers, are some of the primary reasons for the dismal 5-year survival rates (∼8%) in patients with PDAC. The pancreatic cancer develops through accumulation of a series of genomic and epigenomic alterations which lead to the transformation of normal pancreatic epithelium into an invasive carcinoma - a process that can take up to 15-20 years to develop, from the occurrence of first initiating mutational event. These facts highlight a unique window of opportunity for the earlier detection of PDAC, which could allow timely disease interception and improvement in the overall survival outcomes in patients suffering from this fatal malignancy. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have been recognized to play a central role in PDAC pathogenesis and are emerging as attractive candidates for biomarker development in various cancers, including PDAC. More specifically, the ncRNAs play a pivotal role in PDAC biology as they affect tumor growth, migration, and invasion by regulating cellular processes including cell cycle, apoptosis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In this review, we focus on three types of well-established ncRNAs - microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) - and discuss their potential as diagnostic, prognostic and predictive biomarkers in PDAC.
Keywords: Diagnostic biomarkers; Non-coding RNAs; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Predictive biomarkers; Prognostic biomarkers.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None of the authors has any potential conflicts to disclose
Figures
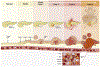
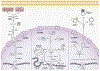
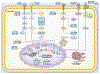

References
-
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program. Cancer stat facts: pancreas cancer., 2019. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html. .
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A, Cancer statistics, 2018, CA Cancer J Clin 68(1) (2018) 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Oettle H, Neuhaus P, Hochhaus A, Hartmann JT, Gellert K, Ridwelski K, Niedergethmann M, Zulke C, Fahlke J, Arning MB, Sinn M, Hinke A, Riess H, Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and long-term outcomes among patients with resected pancreatic cancer: the CONKO-001 randomized trial, JAMA 310(14) (2013) 1473–81. - PubMed
-
- Neoptolemos JP, Stocken DD, Friess H, Bassi C, Dunn JA, Hickey H, Beger H, Fernandez-Cruz L, Dervenis C, Lacaine F, Falconi M, Pederzoli P, Pap A, Spooner D, Kerr DJ, Buchler MW, C. European Study Group for Pancreatic, A randomized trial of chemoradiotherapy and chemotherapy after resection of pancreatic cancer, N Engl J Med 350(12) (2004) 1200–10. - PubMed
-
- Bockhorn M, Uzunoglu FG, Adham M, Imrie C, Milicevic M, Sandberg AA, Asbun HJ, Bassi C, Buchler M, Charnley RM, Conlon K, Cruz LF, Dervenis C, Fingerhutt A, Friess H, Gouma DJ, Hartwig W, Lillemoe KD, Montorsi M, Neoptolemos JP, Shrikhande SV, Takaori K, Traverso W, Vashist YK, Vollmer C, Yeo CJ, Izbicki JR, S. International Study Group of Pancreatic, Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: a consensus statement by the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS), Surgery 155(6) (2014) 977–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

