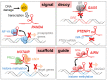
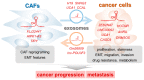
Long Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators of Interactions between Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Cancer Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 33050576
- PMCID: PMC7589653
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21207484
Long Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators of Interactions between Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Cancer Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) regulate diverse physiological and pathological processes via post-transcriptional, post-translational, and epigenetic mechanisms. They are also involved in tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis by functioning as key players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) promote tumor initiation, progression, metastasis, drug resistance, and immunosuppression, which can be modulated by lncRNAs. LncRNAs regulate the intrinsic properties of CAFs or cancer cells intracellularly or function extracellularly through exosomal secretion. In-depth studies on the mechanisms of lncRNA functions will enable their clinical use as diagnosis/prognosis markers and therapeutic targets in cancer treatment.
Keywords: cancer-associated fibroblasts; long non-coding RNAs; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pandey R.R., Mondal T., Mohammad F., Enroth S., Redrup L., Komorowski J., Nagano T., Mancini-Dinardo D., Kanduri C. Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol. Cell. 2008;32:232–246. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.022. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical