Tocilizumab for treating COVID-19: a systemic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies
- PMID: 33051695
- PMCID: PMC7553373
- DOI: 10.1007/s00228-020-03017-5
Tocilizumab for treating COVID-19: a systemic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies
Abstract
Objectives: COVID-19 has become a global epidemic, and effective therapies have not been discovered up to now. We conducted this study to explore the effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab recently used for treating COVID-19.
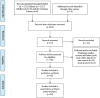
Method: A comprehensive search was conducted (up to September 27, 2020), and 19 eligible records were identified according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The data of the studies were extracted by 2 independent reviewers and were analyzed to evaluate the safety and availability of tocilizumab for treating COVID-19.
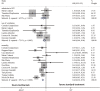
Results: Thirteen retrospective case-control studies (n = 2285 patients) and 6 retrospective single-armed studies (n = 208) were retrieved in this study. In the comparison of tocilizumab treatment group (TCZ) and standard treatment group (ST), significant associations with a lower risk of admission to ICU, use of ventilation, and mortality (OR, 95% CI: 0.53, 0.26~1.09; 0.66, 0.46~0.94; 0.44, 0.36~0.55) were found in the tocilizumab treatment group. What is more, patients treated with tocilizumab had better clinical improvement compared with the patients treated with ST (OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.96~1.62). After taking tocilizumab, the patients had lower C-reactive protein (CRP), white blood cell count (WBC), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (WMD, 95% CI: - 99.66, - 156.24~- 43.09; - 0.95, - 1.8~- 0.11; - 12.58, - 18.88~-6.29) but higher troponin (WMD, 7.61; 95% CI, 3.06~12.15) than before. In addition, tocilizumab did not have significant influence on patients' neutrophil count (Neut), lymphocyte count (Lymp), platelet count (Plt), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and creatine (WMD, 95% CI: - 0.29, - 2.91~2.33; 0.42, - 0.23~1.07; 5.2, - 2.85~13.25; 22.49, - 2.73~47.7; - 44.78, - 93.37~3.81).
Conclusion: Tocilizumab may have potential effectiveness to treat COVID-19 according to the results of this study. However, more large-scale studies are needed for more accurate conclusions.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6 blockade; Meta-analysis; Tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, du B, Li LJ, Zeng G, Yuen KY, Chen RC, Tang CL, Wang T, Chen PY, Xiang J, Li SY, Wang JL, Liang ZJ, Peng YX, Wei L, Liu Y, Hu YH, Peng P, Wang JM, Liu JY, Chen Z, Li G, Zheng ZJ, Qiu SQ, Luo J, Ye CJ, Zhu SY, Zhong NS, China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19 Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1708–1720. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Michot JM, Albiges L, Chaput N, Saada V, Pommeret F, Griscelli F, Balleyguier C, Besse B, Marabelle A, Netzer F, Merad M, Robert C, Barlesi F, Gachot B, Stoclin A. Tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, to treat COVID-19-related respiratory failure: a case report. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(7):961–964. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.300. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lauterio A, Valsecchi M, Santambrogio S et al (2020) Successful recovery from severe COVID-19 pneumonia after kidney transplantation: The interplay between immunosuppression and novel therapy including tocilizumab [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 25]. Transpl Infect Dis:e13334. 10.1111/tid.13334 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

