De-mystifying the "Mixifusor"
- PMID: 33051933
- PMCID: PMC7756545
- DOI: 10.1111/pan.14039
De-mystifying the "Mixifusor"
Abstract
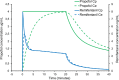
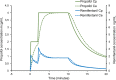
Total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) using a mixture of propofol and remifentanil in the same syringe has become an accepted technique in Pediatric Anesthesia. A survey by a group of respected UK anesthetists demonstrated a low incidence of serious complications, related to the pharmacology and dose of the drugs. However, a current guideline for the safe use of TIVA recommends against this practice. Pharmaceutical concerns include the physical stability of the emulsion when remifentanil is mixed with propofol; changes in drug concentration over time; nonuniform mixing of propofol and remifentanil; the risk of bacterial contamination; and the potential for drug administration errors. Propofol and remifentanil have markedly different pharmacokinetic profiles. When remifentanil is mixed with propofol and delivered as a target-controlled infusion (TCI) of propofol, remifentanil delivery is not target-controlled but passively follows the variable infusion rates calculated by the syringe driver to deliver predicted plasma or effect-site concentrations of propofol. The pharmacokinetic consequences can be illustrated using pharmacokinetic modeling similar to that used in TCI pumps. The clinical consequences reflect the dose-dependent pharmacodynamics of remifentanil. Increasing the target propofol concentration produces a rapid increase and peak in remifentanil concentration that risks apnea, bradycardia, and hypotension, especially with higher concentrations of remifentanil. The faster decline in remifentanil concentration with falling propofol concentrations risks inadequate narcosis and unwanted responses to surgical stimuli. Remifentanil delivery is inflexible and dosing cannot be adjusted to the clinical need and responses of individual patients. The medicolegal considerations are stark. In UK and EU Law, mixing propofol and remifentanil creates a new, unlicensed drug and the person mixing takes on the responsibilities of manufacturer. If a patient receiving anesthesia in the form of a mixed propofol-remifentanil infusion suffered a critical incident or actual harm, the clinician's practice may come under scrutiny and criticism, potentially involving a legal challenge and the Medical Regulator.
Keywords: clinical pharmacology; pharmacokinetics; propofol; remifentanil; safety; target-controlled infusions.
© 2020 The Authors. Pediatric Anesthesia published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
ARA: His research group/department received grants and funding from The Medicines Company (Parsippany, NJ, USA), Becton Dickinson (Eysins, Switzerland), Dräger (Lübeck, Germany), Paion (Aachen, Germany), and Rigel (San Francisco, CA, USA); and he has received honoraria from The Medicines Company (Parsippany, NJ, USA), Janssen Pharmaceutica NV (Beerse, Belgium), Becton Dickinson (Eysins, Switzerland), Paion (Aachen, Germany), Rigel (San Francisco, CA, USA), Philips (Eindhoven, Netherlands), and Ever Pharma (Unterach, Austria). AER‐J: None. ARR: None. JRS: Consultant to Paion (Aachen, Germany) and Altus (Toronto, Canada).
Figures

Comment in
-
Mixing of propofol and remifentanil.Paediatr Anaesth. 2021 Apr;31(4):504-505. doi: 10.1111/pan.14137. Paediatr Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 33772960 No abstract available.
Comment on
-
The safety profile and effectiveness of propofol-remifentanil mixtures for total intravenous anesthesia in children.Paediatr Anaesth. 2020 Dec;30(12):1331-1339. doi: 10.1111/pan.14018. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Paediatr Anaesth. 2020. PMID: 32961621
-
The use of propofol-remifentanil mixture for TIVA in pediatric anesthesia-An opinion from a group of pediatric anesthetists.Paediatr Anaesth. 2021 Apr;31(4):502-503. doi: 10.1111/pan.14135. Paediatr Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 33772954 No abstract available.
References
-
- Morton WD, Lerman J. Technical Report The effect of pancuronium on the solubility of aqueous thiopentone. Can J Anaesth. 1987;34(1):87. - PubMed
-
- Picard P, Tramer MR. Prevention of pain on injection with propofol: a quantitative systematic review. Anest Analg. 2000;90(4):963‐969. - PubMed
-
- Wilson RJ, Ridley SA. The use of propofol and alfentanil by infusion in military anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 1992;47(3):231‐233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

