The biological function and potential mechanism of long non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 33052009
- PMCID: PMC7701533
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15968
The biological function and potential mechanism of long non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular disease
Abstract
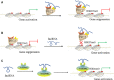
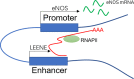
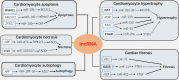
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), as part of the family of non-protein-coding transcripts, are implicated in the occurrence and progression of several cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). With recent advances in lncRNA research, these molecules are purported to regulate gene expression at multiple levels, thereby producing beneficial or detrimental biological effects during CVD pathogenesis. At the transcriptional level, lncRNAs affect gene expression by interacting with DNA and proteins, for example, components of chromatin-modifying complexes, or transcription factors affecting chromatin status. These potential mechanisms suggest that lncRNAs guide proteins to specific gene loci (eg promoter regions), or forestall proteins to specific genomic sites via DNA binding. Additionally, some lncRNAs are required for correct chromatin conformation, which occurs via chromatin looping in enhancer-like models. At the post-transcriptional level, lncRNAs interact with RNA molecules, mainly microRNAs (miRNAs) and mRNAs, potentially regulating CVD pathophysiological processes. Moreover, lncRNAs appear to post-transcriptionally modulate gene expression by participating in mRNA splicing, stability, degradation and translation. Thus, the purpose of this review is to provide a comprehensive summary of lncRNAs implicated in CVD biological processes, with an emphasis on potential mechanisms of action.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; long non-coding RNA; microRNA; post-transcriptional regulation; transcriptional regulation.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that they declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The novel regulatory role of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Dec;22(12):5768-5775. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13866. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30188595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-coding RNA.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017 Jun;15(3):177-186. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.12.005. Epub 2017 May 19. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28529100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs: long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs in endocrine-related cancers.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2018 Apr;25(4):R259-R282. doi: 10.1530/ERC-17-0548. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29440232 Review.
-
Regulation of lncRNA expression.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2014 Dec;19(4):561-75. doi: 10.2478/s11658-014-0212-6. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25311814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding Transcripts from Enhancers: New Insights into Enhancer Activity and Gene Expression Regulation.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017 Jun;15(3):201-207. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Jun 17. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28599852 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Expression of miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs between Ovaries and Testes in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio).Cells. 2023 Nov 15;12(22):2631. doi: 10.3390/cells12222631. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37998366 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of myocardial infarction.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024 Oct 17;55:101529. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101529. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024. PMID: 39498345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Mar;29(5):e70453. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70453. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40032652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and functional prediction of long non-coding RNA and mRNA related to connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung diseases.Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2023 Dec 19;4(4):204-215. doi: 10.2478/rir-2023-0030. eCollection 2023 Dec. Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 38125642 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNAs as prognostic markers and therapeutic targets in cuproptosis-mediated cancer.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Sep 26;24(1):226. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01491-0. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39325172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

