A snake toxin as a theranostic agent for the type 2 vasopressin receptor
- PMID: 33052234
- PMCID: PMC7545998
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.47485
A snake toxin as a theranostic agent for the type 2 vasopressin receptor
Abstract
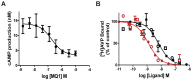
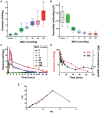
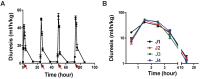
Rationale: MQ1, a snake toxin which targets with high nanomolar affinity and absolute selectivity for the type 2 vasopressin receptor (V2R), is a drug candidate for renal diseases and a molecular probe for imaging cells or organs expressing V2R. Methods: MQ1's pharmacological properties were characterized and applied to a rat model of hyponatremia. Its PK/PD parameters were determined as well as its therapeutic index. Fluorescently and radioactively labeled MQ1 were chemically synthesized and associated with moderate loss of affinity. MQ1's dynamic biodistribution was monitored by positron emission tomography. Confocal imaging was used to observe the labeling of three cancer cell lines. Results: The inverse agonist property of MQ1 very efficiently prevented dDAVP-induced hyponatremia in rats with low nanomolar/kg doses and with a very large therapeutic index. PK (plasma MQ1 concentrations) and PD (diuresis) exhibited a parallel biphasic decrease. The dynamic biodistribution showed that MQ1 targets the kidneys and then exhibits a blood and kidney biphasic decrease. Whatever the approach used, we found a T1/2α between 0.9 and 3.8 h and a T1/2β between 25 and 46 h and demonstrated that the kidneys were able to retain MQ1. Finally, the presence of functional V2R expressed at the membrane of cancer cells was, for the first time, demonstrated with a specific fluorescent ligand. Conclusion: As the most selective V2 binder, MQ1 is a new promising drug for aquaresis-related diseases and a molecular probe to visualize in vitro and in vivo V2R expressed physiologically or under pathological conditions.
Keywords: PET imaging; PK/PD; Snake toxin; cancers; theranostic agent.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


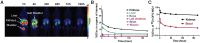
References
-
- Birnbaumer M, Seibold A, Gilbert S, Ishido M, Barberis C, Antaramian A. et al. Molecular cloning of the receptor for human antidiuretic hormone. Nature. 1992;357:333–5. - PubMed
-
- Bankir L. Antidiuretic action of vasopressin: quantitative aspects and interaction between V1a and V2 receptor-mediated effects. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;51:372–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

