This is a preprint.
Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model
- PMID: 33052329
- PMCID: PMC7553153
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-86289/v1
Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model
Update in
-
Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 16;12(1):2295. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22580-8. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33863887 Free PMC article.
Abstract
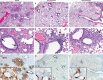
The COVID-19 pandemic progresses unabated in many regions of the world. An effective antiviral against SARS-CoV-2 that could be administered orally for use following high-risk exposure would be of substantial benefit in controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. Herein, we show that MK-4482, an orally administered nucleoside analog, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model. The inhibitory effect of MK-4482 on SARS-CoV-2 replication was observed in animals when the drug was administered either beginning 12 hours before or 12 hours following infection in a high-risk exposure model. These data support the potential utility of MK-4482 to control SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans following high-risk exposure as well as for treatment of COVID-19 patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
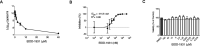


References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. Vol. 2020 (2020).
-
- Gibney E. Whose coronavirus strategy worked best? Scientists hunt most effective policies. Nature 581, 15–16 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

