Metabolomic profile of cancer stem cell-derived exosomes from patients with malignant melanoma
- PMID: 33052601
- PMCID: PMC7858120
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12823
Metabolomic profile of cancer stem cell-derived exosomes from patients with malignant melanoma
Abstract
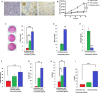
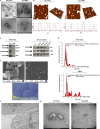
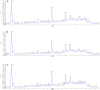
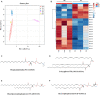
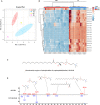
Malignant melanoma (MM) is the most aggressive and life-threatening form of skin cancer. It is characterized by an extraordinary metastasis capacity and chemotherapy resistance, mainly due to melanoma cancer stem cells (CSCs). To date, there are no suitable clinical diagnostic, prognostic or predictive biomarkers for this neoplasia. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new MM biomarkers that enable early diagnosis and effective disease monitoring. Exosomes represent a novel source of biomarkers since they can be easily isolated from different body fluids. In this work, a primary patient-derived MM cell line enriched in CSCs was characterized by assessing the expression of specific markers and their stem-like properties. Exosomes derived from CSCs and serums from patients with MM were characterized, and their metabolomic profile was analysed by high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) following an untargeted approach and applying univariate and multivariate statistical analyses. The aim of this study was to search potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of this disease. Our results showed significant metabolomic differences in exosomes derived from MM CSCs compared with those from differentiated tumour cells and also in serum-derived exosomes from patients with MM compared to those from healthy controls. Interestingly, we identified similarities between structural lipids differentially expressed in CSC-derived exosomes and those derived from patients with MM such as the glycerophosphocholine PC 16:0/0:0. To our knowledge, this is the first metabolomic-based study aimed at characterizing exosomes derived from melanoma CSCs and patients' serum in order to identify potential biomarkers for MM diagnosis. We conclude that metabolomic characterization of CSC-derived exosomes sets an open door to the discovery of clinically useful biomarkers in this neoplasia.
Keywords: biomarkers; cancer stem cells; exosomes; malignant melanoma; metabolomics.
© 2020 The Authors. Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allegra A, Alonci A, Penna G, Innao V, Gerace D, Rotondo F & Musolino C (2014) The cancer stem cell hypothesis: a guide to potential molecular targets. Cancer Invest 32, 470–495. - PubMed
-
- Islam F, Gopalan V, Smith RA & Lam AK‐Y (2015) Translational potential of cancer stem cells: a review of the detection of cancer stem cells and their roles in cancer recurrence and cancer treatment. Exp Cell Res 335, 135–147. - PubMed
-
- Hernández‐Camarero P, Jiménez G, López‐Ruiz E, Barungi S, Marchal JA & Perán M (2018) Revisiting the dynamic cancer stem cell model: importance of tumour edges. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 131, 35–45. - PubMed
-
- Civenni G, Walter A, Kobert N, Mihic‐Probst D, Zipser M, Belloni B, Seifert B, Moch H, Dummer R, van den Broek M et al (2011) Human CD271‐positive melanoma stem cells associated with metastasis establish tumor heterogeneity and long‐term growth. Cancer Res 71, 3098–3109. - PubMed

